Chapter 9.100
Definitions
Sections:
9.100.020 Definitions of Specialized Terms and Phrases
9.100.010 Purpose
This Chapter provides definitions of terms and phrases used in this Land Use Code that are technical or specialized, or that may not reflect common usage. If any of the definitions in this Chapter conflict with definitions in other provisions of the Municipal Code, these definitions shall control for the purposes of this Land Use Code. If a word is not defined in this Chapter, or in other provisions of the City of Arcata Municipal Code, the Director shall determine the correct definition.
9.100.020 Definitions of Specialized Terms and Phrases
As used in this Land Use Code, the following terms and phrases shall have the meaning ascribed to them in this Section, unless the context in which they are used clearly requires otherwise.
A Definitions, "A."
Abut. Having property lines, street lines, or zoning district lines in common.
Accessory Dwelling Unit. An attached or a detached residential dwelling unit that provides complete independent living facilities for one or more persons. It shall include permanent provisions for living, sleeping, eating, cooking, and sanitation on the same parcel as the single-family dwelling is situated. An accessory dwelling unit also includes an efficiency unit, as defined in Section 17958.1 of Health and Safety Code, and a manufactured home, as defined in Section 18007 of the Health and Safety Code. See also, "Residential Accessory Use" or "Structure" and "Second Unit."
Accessory Retail or Services. The retail sale of various products, or the provision of certain personal services within a health care, hotel, office, or industrial complex, to employees or customers. Examples of these uses include pharmacies, gift shops, and food service establishments within hospitals; convenience stores and food service establishments within hotel, office and industrial complexes; and barber and beauty shops within residential care facilities.
Accessory Structure. A structure that is physically attached or detached from, secondary and incidental as measured by mass, size or location to, and commonly associated with a primary structure on the same site. See also "Agricultural Accessory Structure," "Garage" and "Residential Accessory Uses and Structures."
Accessory Use. A use customarily incidental to, related and clearly subordinate to a primary use on the same parcel, which does not alter the primary use.
Acres, Gross. The entire acreage of a site. Gross acreage is calculated to the centerline of proposed bounding streets and to the edge of the right-of-way of existing or dedicated streets.
Acres, Net. The portion of a site that can actually be built upon. The following generally are not included in the net acreage of a site: public or private road rights-of-way, public open space, and flood ways.
Adaptive Use/Reuse. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Adequate Solar Access. See "Solar Access."
Revised Ord. # 1382 - Effective 12/22/08
Adult day care facility. See "Day Care."
Affordable and Inclusionary Housing. The following terms and phrases are defined for the purposes of Chapter 9.31 and 9.32:
1. Affordable Sales Price (Single Family Residential Projects). "Affordable" means average monthly housing payments, including mortgage loan principal and interest, any associated loan insurance fees, property taxes and assessments, homeowners insurance, land rent (if the home is on rented or ground lease land) and homeowners association dues, if any, which during the first (1st) calendar year of a household’s occupancy, are equal to or less than: (i) for Very Low Income Inclusionary Units, one-twelfth (1/12th) of forty-two percent (42%) of fifty percent (50%) of Median Income, adjusted by household size based on the number of bedrooms in the unit; (ii) for Low Income Inclusionary Units, one-twelfth (1/12th) of forty-two percent (42%) of seventy-two percent (72%) of Median Income, adjusted for household size based on the number of bedrooms in the unit; and (iii) for Moderate Income Inclusionary Units, one-twelfth (1/12th) of forty-two percent (42%) of one hundred ten percent (110%) of Median Income, adjusted for household size based on the number of bedrooms in the unit. Adjustments for household sized based on the number of bedrooms in the unit and amounts utilized for utility allowances and other monthly housing cost factors, including assumed mortgage interest rates, loan insurance fees, maintenance and repair allowances, homeowners’ insurance, property tax and assessment costs, and homeowners association dues, shall be as provided by the City’s First Time Homebuyer Guidelines.
2. Affordable Rent (Multi-Family Residential Projects). "Affordable" means rents calculated annually by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development ("HUD") and are:
a. The lesser of the Fair Market Rents or a rent that does not exceed thirty percent (30%) of sixty percent (60%) of the area median income ("Low Income Rents"); or
b. Thirty percent (30%) of fifty percent (50%) of the area median income ("Very -Low Rents").
c. Other rent levels that may be established by the City Council for a specific project or program.
3. Affordable Unit. A dwelling unit that is required to be rented at affordable rents or purchased at an affordable sales price to specified households.
4. Annual Household Income. The combined gross income for all adult persons living in a dwelling unit as calculated for the purpose of the Section 8 program under the United States Housing Act of 1937, as amended, or its successor, or other income limits that may be required by a public funding agency.
5. Assisted Housing. Generally multi-family rental housing, but sometimes single-family ownership units, whose construction, financing, sales prices, or rents have been subsidized by federal, state, or local housing programs including, but not limited to Federal ’8 (new construction, substantial rehabilitation, and loan management set-asides), Federal ’s 213, 236, and 202, Federal ’221(d)(3) (below-market interest rate program), Federal ’101 (rent supplement assistance), CDBG, FmHA’515, multi-family mortgage revenue bond programs, local redevelopment and in lieu fee programs, and units developed pursuant to local inclusionary housing and density bonus programs.
6. Construction Costs. The estimated cost per square foot of construction, as established by the Building Official for use in setting regulatory fees and Building Permits, multiplied by the total square footage, to be constructed, except for any floor area devoted to a garage.
7. Density Bonus. As defined by Government Code Section 65915 et seq., an increase over the maximum density otherwise allowed by the applicable zoning district, that is granted to the owner/developer of a housing project who agrees to construct a senior housing project or a prescribed percentage of dwelling units that are affordable to households of very low; low; and/or moderate income. When determining the number of dwelling units that shall be affordable, the units authorized by the density bonus shall not be included in the calculation.
8. External Subsidy. Any source of funds that is not local public funding, including Federal or state grants, loans, bond funds, tax credits or other tax-based subsidy.
9. First-Time Home Buyer. A home buyer who has not (nor has his/her spouse) owned a home during the past three years, or that the purchaser meets at least one of the following criteria:
a. The purchaser is a displaced homemaker as defined as an individual who is an adult; has not worked full time, full year in the labor force for a number of years but has, during such years, worked primarily without remuneration to care for the home and is unemployed or underemployed and experiencing difficulty in obtaining or upgrading employment.
b. The purchaser is a single parent as defined as an individual who is unmarried or legally separated from a spouse; and has one or more minor children for whom the individual has custody or joint custody; or is pregnant, may not be excluded from consideration as a first time homebuyer on the basis that the individual, while married, owned a home with his or her spouse or resided in a home owned by the spouse.
c. The purchaser owns or owned as a principal residence during the past three years, a dwelling unit which structure is not permanently affixed to a permanent foundation in accordance with the City Code, or is not and cannot be brought into compliance with City Code for less than the cost of replacing the structure.
10. Housing Trust Fund. The fund created by the City as per Implementation Measure HE-27 of the City’s Housing Element to retain funds collected in a segregated account specifically to assist with the development of affordable housing.
11. Affordable Housing Regulatory Agreement, or Agreement. The agreement described in Section 9.32.110 between a developer and the City setting forth the manner in which required inclusionary units will be provided in a proposed residential project.
12. Inclusionary Housing Plan. The plan described in Section 9.32.110 setting forth the manner in which required inclusionary units will be implemented in a residential project.
13. Inclusionary Incentives. Fee waivers or reductions, planning and building standards waivers or reductions, regulatory incentives or concessions, and local public funding provided by the City or to a residential project to assist in the provision of inclusionary units.
14. Inclusionary Unit. An ownership or rental dwelling unit developed as a part of a residential project in compliance with this Chapter.
15. Initial Owner. The first person or persons to purchase a new for-sale inclusionary unit for his, her or their primary residence.
16. Legislative Entitlement. Includes General Plan and Land Use Code designations and re-designations, zonings and rezoning, planned unit developments ("PUD"); conditional use permits, variances; and amendments thereto.
17. Low Income Household. A household with an annual income usually no greater than 80 percent of the area median family income adjusted by household size, as determined by a survey of incomes conducted by a city or a county, or in the absence of such a survey, based on the latest available eligibility limits established by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) for the Section 8 housing program.
18. Low-Income Housing Tax Credits. Tax reductions provided by the federal and State governments for investors in housing for low-income households.
19. Market Rate. Not restricted to an affordable housing price or affordable rent.
20. Maximum Allowable Residential Density. The density allowed under the zoning ordinance, or if a range of density is permitted, the maximum allowable density for the specific zoning range applicable to the project.
21. Moderate Income Household. A household with an annual income usually no greater than 120 percent of the area median family income adjusted by household size, as determined by a survey of incomes conducted by a city or a county, or in the absence of such a survey, based on the latest available eligibility limits established by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) for the Section 8 housing program.
22. Off-Site. Outside of the boundaries of a residential project.
23. Owner. The person, persons, partnership, joint venture, association, corporation, or public or private entity having sufficient proprietary interest in real property to commence, maintain, and operate a residential project.
24. Subsidize. To assist by payment of a sum of money or by the granting of terms or favors that reduces the need for monetary expenditures. Housing subsidies may take the forms of mortgage interest deductions or tax credits from federal and/or state income taxes, sale or lease at less than market value of land to be used for the construction of housing, payments to supplement a minimum affordable rent, and the like.
25. Substantial Rehabilitation. The repair, preservation, and/or the improvement of a housing unit where the cost as determined by the Building Official exceeds 50% of the after rehabilitation assessed value of the structure.
26. Very Low Income Household. A household with an annual income usually no greater than 50 percent of the area median family income adjusted by household size, as determined by a survey of incomes conducted by a city or a county, or in the absence of such a survey, based on the latest available eligibility limits established by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) for the Section 8 housing program.
Agent. A person authorized in writing by the property owner to represent and act for a property owner in contacts with City employees, committees, Commissions, and the Council, regarding matters regulated by this Land Use Code.
Agricultural Accessory Structure. A structure for sheltering animals, or agricultural equipment, hay, feed, etc. Examples of these structures include barns, non-commercial greenhouses and coops. May also include the storage of petroleum products for an on-site agricultural use allowed by the applicable zoning district. Does not include pasture fencing, corrals or pens which requires no City approval when in compliance with Section 9.30.030 (Fences, Walls, and Screening).
Agricultural Land. All that real property within the boundaries of the City of Arcata currently used for the production of food, fiber, or livestock or lands upon which agricultural uses may in the future be established.
Agricultural Preserve. Land designated for agriculture or conservation under the "Williamson Act."
Agricultural Processing - Moderate Impact.
|
• Creameries and dairy products manufacturing • Dry - lot livestock operation • Retail sales as an accessory use to a moderate impact agricultural processing |
|
• Low and Moderate Impact processing in covered facilities over 4,000 square feet |
Agricultural Processing - Low Impact. The processing of food, beverages, and harvested crops to prepare them for on-site marketing, off-site sales, or processing and packaging elsewhere. Examples of this land use activity include the following:
|
• Fats and oil product manufacturing • Fruit and vegetable canning, preserving and related processing • Grain mill products and by-product processing • Meat, poultry, fish and seafood canning, curing and by-products manufacturing |
|
• Miscellaneous food and beverage preparation from raw products. • Retail sales as an accessory use to low impact agricultural processing |
Does not include wineries, which are separately defined.
Agricultural Processing - Very Low Impact. The producing and processing of food, beverages, and harvested crops for on-site use, on-site marketing, or processing and packaging elsewhere. Examples of this land use activity include the following:
|
• Corn shelling • Custom grist mills • Dairies (excluding dry-lot livestock operations) • Drying and storage of corn, rice, hay, fruits and vegetables • Grain cleaning and custom grinding • Flower and bulb sorting and packaging |
|
• Hay baling and cubing • Pre-cooling, storage, and packaging of fresh or farm-dried fruits and vegetables • Silage production • Sorting, grading and packaging of fruits and vegetables • Tree nut hulling and shelling |
Agricultural Uses. The cultivation and tillage of the soil; dairying; the production, irrigation, frost protection, cultivation, growing, harvesting and processing of any agricultural commodity, including viticulture, horticulture, timber or apiculture; the raising of livestock, fur bearing livestock, fish or poultry; and any commercial agricultural practices performed as incidental to or in conjunction with such operations, including preparation for market, delivery to storage or to market, or to carriers for transportation to market.
Agriculture. Use of land for the production of food and fiber, including the growing of crops and/or the grazing of animals on natural prime or improved pasture land.
Alcoholic Beverage Sales. The retail sale of beer, wine, and/or distilled spirits for on-premise or off-premise consumption.
Alquist-Priolo Act, Earthquake Fault Zone. A state designated seismic hazard zone along traces of potentially and recently active faults, in which specialized geologic investigations must be prepared prior to approval of certain types of new development.
Alley. A public or private roadway that is not intended for general traffic circulation providing vehicle access to the rear or side of parcels having other public street frontage.
Allowed Use. A use of land identified by Article 2 (Zoning Districts and Allowable Land Uses) as a permitted or conditional use that may be established with planning permit and, where applicable, Design Review and/or Building Permit approval, subject to compliance with all applicable provisions of this Land Use Code.
Alteration. Any construction or physical change in the internal arrangement of rooms or the supporting members of a structure, or a change in the external appearance of any structure, not including painting.
Alteration of a Historic Resource. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Ambient. Surrounding on all sides; used to describe measurements of existing conditions with respect to traffic, noise, air and other environments.
Ambulance, Taxi, or Limousine Dispatch Facility. A base facility from which taxis and limousines are dispatched, and/or where ambulance vehicles and crews stand by for emergency calls.
Animal Keeping. See Section 9.42.050 (Animal Keeping).
Annex. To incorporate a land area into an existing district or municipality, with a resulting change in the boundaries of the annexing jurisdiction.
Annual Household Income. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Apartment. See "Multi-Family Housing."
Applicant. Any person who is filing an application requesting an action who is:
1. The owner or lessee of property;
2. A party who has contracted to purchase property contingent upon that party’s ability to acquire the necessary approvals required for that action in compliance with this Land Use Code, and who presents written authorization from the property owner to file an application with the City; or
3. The agent of either of the above who presents written authorization from the property owner to file an application with the City.
Approval. Includes both approval and approval with conditions.
Aquaculture. The raising and harvesting of aquatic organisms, including shellfish, mollusks, crustaceans, kelp, and algae, in close proximity to the ocean, and dependent on ocean water.
Aquifer. An underground, water-bearing layer of earth, porous rock, sand, or gravel, through which water can seep or be held in natural storage. Aquifers generally hold sufficient water to be used as a water supply.
Arable. Land capable of being cultivated for farming.
Archeological Site. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Architectural Feature. An exterior building feature including roof, windows, doors, porches, etc.
Arterial. Medium-speed (30-40 mph), medium-capacity (10,000-35,000 average daily trips) roadway that provides intra-community travel and access to the county-wide highway system. Access to community arterials should be provided at collector roads and local streets, but direct access from parcels to existing arterials is common.
Artificial Wetlands. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Artisan Shop. A retail store selling art glass, ceramics, jewelry, paintings, sculpture, and other handcrafted items, where the facility includes an area for the crafting of the items being sold.
Assessed Value. The value of a structure as shown in the records of the County Assessor.
Assessment District. (See "Benefit Assessment District.")
Assisted Housing. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Assisted Living Facility. See "Residential Care Facility for the Elderly (RCFE)."
Attainment. Compliance with State and federal ambient air quality standards within an air basin. (See "Non-attainment.")
Attic. The area located between the uppermost plate and the roof or ridge of a structure.
Auto and Vehicle Sales/Rental. A retail or wholesale establishment selling and/or renting automobiles, trucks and vans, trailers, motorcycles, and bicycles (bicycle sales are also included under "General Retail"). May also include repair shops and the sales of parts and accessories, incidental to vehicle dealerships. Does not include: the sale of auto parts/accessories separate from a vehicle dealership (see "Auto Parts Sales"); mobile home, recreational vehicle, or watercraft sales (see "Mobile Home, RV and Boat Sales"); tire recapping establishments (see "Vehicle Services"); businesses dealing exclusively in used parts, (see "Recycling - Scrap and Dismantling Yards"); or "Service Stations," which are separately defined.
Auto Parts Sales. Stores that sell new automobile parts, tires, and accessories. Establishments that provide installation services are instead included under "Vehicle Services - Repair and Maintenance - Minor." Does not include tire recapping establishments, which are found under "Vehicle Services" or businesses dealing exclusively in used parts, which are included under "Recycling - Scrap and Dismantling Yards."
Auto Repair. See "Vehicle Services."
Automated Teller Machine (ATM). Computerized, self-service machines used by banking customers for financial transactions, including deposits, withdrawals and fund transfers, without face-to-face contact with financial institution personnel. The machines may be located at or within banks, or in other locations.
Average Low Flow Line. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
B Definitions, "B."
Bank, Financial Services. Financial institutions including:
|
• banks and trust companies • credit agencies • holding (but not primarily operating) companies • lending and thrift institutions • other investment companies |
|
• securities/commodity contract brokers and dealers • security and commodity exchanges • vehicle finance (equity) leasing agencies |
See also, "Automated Teller Machine."
Banner, Flag, or Pennant. See "Sign."
Bar/Tavern/Pub. A business where alcoholic beverages are sold for on-site consumption, which are not part of a larger restaurant. Includes bars, taverns, pubs, and similar establishments where any food service is subordinate to the sale of alcoholic beverages. May also include beer brewing as part of a microbrewery ("brew-pub"), and other beverage tasting facilities. Does not include sex oriented businesses.
Base Zone. The primary, underlying zone district.
Bed and Breakfast Inn (B&B). See "Lodging."
Benefit Assessment District. A geographic area in which there is an annual assessment on real property to provide benefits for the area. The assessment is used to pay the costs of providing specific park capital improvements, fire, flood, water, sewer and other community services.
Benefited Property. See "Solar Access."
Bicycle Lane (Class II facility). A corridor expressly reserved for bicycles, existing on a street or roadway in addition to any lanes for use by motorized vehicles.
Bicycle Path (Class I facility). A paved route not on a street or roadway and expressly reserved for bicycles traversing an otherwise unpaved area. Bicycle paths may parallel roads but typically are separated from them by landscaping.
Bicycle Route (Class III facility). A facility shared with motorists and identified only by signs, a bicycle route has no pavement markings or lane stripes.
Bikeways. A term that encompasses bicycle lanes, bicycle paths, and bicycle routes.
Biodiversity. The variety of organisms considered at all levels, from genetic variants belonging to the same species, through arrays of species to arrays of genera, families, and still higher taxonomic levels; includes the variety of ecosystems, which comprise both the communities of organisms within particular habitats and the physical conditions under which they live.
Boat Launching Facility. An area with facilities and equipment for the placement of boats in the ocean. May include launching ramps, hoists, piers, and onshore parking areas for boat trailers and other vehicles.
Bond. An interest-bearing promise to pay a stipulated sum of money, with the principal amount due on a specific date. Funds raised through the sale of bonds can be used for various public purposes.
Broadcasting Studio. Commercial and public communications use including radio and television broadcasting and receiving stations and studios, with facilities entirely within buildings. Does not include transmission and receiving apparatus, including antennas and towers, which are instead defined under "Telecommunications Facilities".
Brownfield. An area with abandoned, idle, or under-used industrial and commercial facilities where expansion, redevelopment, or reuse is complicated by real or perceived environmental contamination. (See "Greenfield.")
Buffer Zone. An area of land separating two distinct land uses that acts to soften or mitigate the effects of one land use on the other.
Buildable Area. The portion of a site that can actually be built upon and which is outside of identified site constraints that are specified within this Land Use Code.
Building and Landscape Materials Sales. A retail establishment selling hardware, lumber and other large building materials, plant materials, and other landscaping materials. Includes paint, wallpaper, glass, and fixtures. Includes all these stores selling to the general public, even if contractor sales account for a major proportion of total sales. Establishments primarily selling electrical, plumbing, heating, and air conditioning equipment and supplies are classified in "Wholesaling and Distribution."
Building Height. See Section 9.30.040 (Height Limits and Exceptions).
Building Official. The City of Arcata Building Official, or designee of the Building Official.
Buildout; Build-out. Development of land to its full potential or theoretical capacity as permitted under current or proposed planning or zoning designations. (See "Carrying Capacity (3).")
Burdened Property. See "Solar Access."
Business Support Service. An establishment within a building that provides services to other businesses. Examples of these services include:
|
• blueprinting • computer-related services (rental, repair) • copying and quick printing services • film processing and photofinishing (retail) |
|
• outdoor advertising services • mailing and mail box services • protective services (other than office related) • security systems services |
Busway. A vehicular right-of-way or portion thereof-often an exclusive lane-reserved exclusively for buses.
C Definitions, "C."
Cabinet Shop. See "Furniture and Fixtures Manufacturing, Cabinet Shops."
California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA). State law (California Public Resources Code Sections 21000 et seq.) requiring public agencies to document and consider the environmental effects of a proposed action, prior to allowing the action to occur.
California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC). The governmental agency which regulates the terms and conditions of public utilities in the State.
Caltrans. California Department of Transportation.
Campground. See "Lodging."
Cannabis. All parts of the plant Cannabis sativa Linnaeus, Cannabis indica, or Cannabis ruderalis, whether growing or not; the seeds thereof; the resin, whether crude or purified, extracted from any part of the plant; and every compound, manufacture, salt, derivative, mixture, or preparation of the plant, its seeds, or resin. "Cannabis" also means: (1) "marijuana" as defined by Section 11018 of the Health and Safety Code, and (2) the separated resin, whether crude or purified, obtained from marijuana. "Cannabis" does not include the mature stalks of the plant, fiber produced from the stalks, oil or cake made from the seeds of the plant, any other compound, manufacture, salt, derivative, mixture, or preparation of the mature stalks (except the resin extracted therefrom), fiber, oil, or cake, or the sterilized seed of the plant which is incapable of germination. For the purpose of this Chapter, "cannabis" does not mean "industrial hemp" as defined by Section 81000 of the Food and Agricultural Code or Section 11018.5 of the Health and Safety Code.
Cannabis Retail Sales and Service Facility. A business where cannabis products are sold to a consumer for on- or off-site consumption or use. Cannabis services include businesses using cannabis products as part of a service to consumers such as a beauty/barber shop, massage parlor, counseling, and similar establishments.
Capital Improvements Program (CIP). A program established by a city or county government and reviewed by its planning commission, which schedules permanent improvements, usually for a minimum of five years in the future, to fit the projected fiscal capability of the local jurisdiction. The program generally is reviewed annually, for conformance to and consistency with the general plan.
Card Room. An establishment offering legal gambling activities in compliance with a State license.
Caretaker/Employee Unit. A permanent residence that is secondary or accessory to the primary use of the property, and used for housing a caretaker employed on the site of any non-residential use where needed for security purposes or to provide 24-hour care or monitoring of people, plants, animals, equipment, or other conditions on the site.
Carport. See "Garage, or Carport."
Carriage House. A secondary residential unit located over a detached garage.
Carrying Capacity. Used in determining the potential of an area to absorb development: (1) The level of land use, human activity, or development for a specific area that can be accommodated permanently without an irreversible change in the quality of air, water, land, or plant and animal habitats. (2) The upper limits of development beyond which the quality of human life, health, welfare, safety, or community character within an area will be impaired. (3) The maximum level of development allowable under current zoning. (See "Buildout.")
Catering Service. A business that prepares food for consumption on the premises of a client.
Cemetery, Mausoleum, Columbarium. An interment establishment engaged in subdividing property into cemetery lots and offering burial plots or air space for sale. Includes animal cemeteries; cemetery, mausoleum, crematorium and columbarium operations, and full-service mortuaries and funeral parlors accessory to a cemetery or columbarium.
Central Business District (CBD). The major commercial downtown center of a community. General guidelines for delineating a downtown area are defined by the U.S. Census of Retail Trade, with specific boundaries being set by the local municipality.
Change of Use. The replacement of an existing use on a lot or parcel, or any portion thereof, by a new use, or a change in the nature of an existing use; but does not include a change of ownership, tenancy, or management associated with a use for which the previous nature of the use will remain substantially unchanged.
Channel or Drainage Way. See "Grading."
Channelization. (1) The straightening and/or deepening of a watercourse for purposes of storm-runoff control or ease of navigation. Channelization often includes lining of stream banks with a retaining material such as concrete. (2) At the intersection of roadways, the directional separation of traffic lanes through the use of curbs or raised islands that limit the paths that vehicles may take through the intersection.
Child Day Care Center. See "Day Care."
City. The City of Arcata, State of California, referred to in this Land Use Code as the "City."
City Council. The Arcata City Council, referred to in this Land Use Code as the "Council."
Club, Lodge, Private Meeting Hall. Permanent, headquarters-type and meeting facilities for organizations operating on a membership basis for the promotion of the interests of the members, including facilities for:
|
• business associations • civic, social and fraternal organizations • labor unions and similar organizations |
|
• political organizations • professional membership organizations • other membership organizations |
Includes grange halls and similar facilities.
Clustered Development. Development in which a number of dwelling units are placed in closer proximity than usual, or are attached, with the purpose of retaining an open space area.
Coastal Access Trail. A public walkway providing pedestrian access to, or along the ocean coastline (vertical, or lateral access, respectively.
Coastal Creek Zone. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Collection Facility. See "Recycling Facility."
Collector. Relatively-low-speed (25-30 mph), relatively-low-volume (5,000-20,000 average daily trips) street that provides circulation within and between neighborhoods. Collectors usually serve short trips and are intended for collecting trips from local streets and distributing them to the arterial network.
Commercial. A land use classification that permits facilities for buying and selling of commodities and services.
Commercial Recreation Facility - Indoor. Establishments providing indoor amusement and entertainment services for a fee or admission charge, including:
|
• bowling alleys • coin-operated amusement arcades • dance halls, clubs and ballrooms • electronic game arcades (video games, pinball, etc.) |
|
• ice skating and roller skating • pool and billiard rooms as primary uses |
This use does not include sex oriented businesses, which are separately defined. Four or more electronic games or coin-operated amusements in any establishment, or a premises where 50 percent or more of the floor area is occupied by amusement devices, are considered an electronic game arcade as described above; three or fewer machines are not considered a land use separate from the primary use of the site.
Commercial Recreation Facility - Outdoor. A facility for various outdoor recreational activities, where a fee is charged for use. Examples include:
|
• amusement and theme parks • go-cart tracks • golf driving ranges |
|
• miniature golf courses • water slides |
May also include commercial facilities customarily associated with the above outdoor commercial recreational uses, including bars and restaurants, video game arcades, etc.
Commercial Strip. Commercial development, usually one store deep, that fronts on a major street for a distance of one city block or more. Includes individual buildings on their own lots, with or without on-site parking, and small linear shopping centers with shallow on-site parking in front of the stores.
Commercial Zoning District. Any of the commercial zoning districts established by Section 9.12.020 (Zoning Map and Zoning Districts).
Community Apartment Project. A development in which an undivided interest in land is coupled with the right of exclusive occupancy of any apartment located thereon.
Community Center. A multi-purpose meeting and recreational facility typically consisting of one or more meeting or multi-purpose rooms, kitchen and/or outdoor barbecue facilities, that are available for use by various groups for such activities as meetings, parties, receptions, dances, etc.
Community Child Care Agency. A non-profit agency established to organize community resources for the development and improvement of child care services.
Community Development Block Grant (CDBG). A grant program administered by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) on a formula basis for entitlement communities, and by the State Department of Housing and Community Development (HCD) for non-entitled jurisdictions such as Arcata. This grant allots money for housing rehabilitation and community development, including public facilities and economic development.
Community Noise Equivalent Level (CNEL). A 24-hour energy equivalent level derived from a variety of single-noise events, with weighting factors of 5 and 10 dBA applied to the evening (7 PM to 10 PM) and nighttime (10 PM to 7 AM) periods, respectively, to allow for the greater sensitivity to noise during these hours.
Community Park. Land with full public access intended to provide recreation opportunities beyond those supplied by neighborhood parks. Community parks are larger in scale than neighborhood parks but smaller than regional parks.
Community Redevelopment Agency (CRA). A local agency created under California Redevelopment Law (Health & Safety code ’33000, et. Seq.), or a local legislative body that has been elected to exercise the powers granted to such an agency, for the purpose of planning, developing, re-planning, redesigning, clearing, reconstructing, and/or rehabilitating all or part of a specified area with residential, commercial, industrial, and/or public (including recreational) structures and facilities. The redevelopment agency’s plans must be compatible with adopted community general plans.
Community Service District (CSD). A geographic subarea of a city or county used for the planning and delivery of parks, recreation, and other human services based on an assessment of the service needs of the population in that subarea. The CSD is a taxation district with independent administration.
Composting. Storage and processing of vegetative materials that relies on natural decay processes to produce soil amendment and nutritive materials.
Condominium. As defined by Civil Code Section 915, a development where undivided interest in common in a portion of real property is coupled with a separate interest in space called a unit, the boundaries of which are described on a recorded final map or parcel map.
Conference/Convention Facility. One or more structures accommodating multiple assembly, meeting, and/or exhibit rooms, and related support facilities (e.g., kitchens, offices, etc.).
Congestion Management Plan (CMP). A mechanism employing growth management techniques, including traffic level of service requirements, standards for public transit, trip reduction programs involving transportation systems management and jobs/ housing balance strategies, and capital improvement programming, for the purpose of controlling and/or reducing the cumulative regional traffic impacts of development.
Congregate Care. Apartment housing, usually for seniors, in a group setting that includes independent living and sleeping accommodations in conjunction with shared dining and recreational facilities.
Conservation Easement. See "Historical Resource Preservation" for "Historic Conservation Easement", and see "Easement, Conservation."
Consistency, Consistent With. Free from significant variation or contradiction. The various diagrams, text, goals, policies, and programs in the general plan must be consistent with each other, not contradictory or preferential. The term "consistent with" is used interchangeably with "conformity with." The courts have held that the phrase "consistent with" means "agreement with; harmonious with." Webster defines "conformity with" as meaning harmony, agreement when used with "with." The term "conformity" means in harmony therewith or agreeable to (Sec 58 Ops.Cal.Atty.Gen. 21, 25 [1975]). California State law also requires that a general plan be internally consistent and also requires consistency between a general plan and implementation measures such as the zoning ordinance. As a general rule, an action program or project is consistent with the general plan if, considering all its aspects, it will further the objectives and policies of the general plan and not obstruct their attainment.
Construction Contractors. Office, and indoor and/or outdoor storage facilities operated by, or on behalf of a contractor licensed by the State of California for storage of large equipment, vehicles, and/or other materials commonly used in the individual contractor’s type of business; storage of scrap materials used for repair and maintenance of contractor’s own equipment; and buildings or structures for uses such as repair facilities.
Construction Costs. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Construction/Heavy Equipment Sales and Rental. Retail establishments selling or renting construction, farm, or other heavy equipment. Examples include cranes, earth moving equipment, tractors, combines, heavy trucks, etc.
Construction Site. The area where new construction, or reconstructing, remodeling, or restoring of an existing structure or site is occurring. This includes the development site and onsite area used by the contractor. This does not include ongoing operations such as permitted industrial activities.
Convenience Store. A retail store of 3,500 square feet or less in gross floor area, which carries a range of merchandise oriented to the convenience shopping needs of nearby residents.
County. The County of Humboldt, State of California.
Covenants, Conditions, and Restrictions (CC&Rs). A term used to describe restrictive limitations that may be placed on property and its use, and which usually are made a condition of holding title or lease.
Creek Zone. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Critical Facility. Facilities housing or serving many people, that are necessary in the event of an earthquake or flood, such as hospitals, fire, police, and emergency service facilities, utility "lifeline" facilities, such as water, electricity, and gas supply, sewage disposal, and communications and transportation facilities.
Crop Production, Horticulture, Orchard, Vineyard. Commercial agricultural production field and orchard uses, including the production of the following, primarily in the soil on the site and not in containers, other than for initial propagation prior to planting in the soil on the site:
|
• field crops • flowers and seeds • fruits • grains • melons • hay |
|
• ornamental crops • tree nuts • trees and sod • vegetables • wine and table grapes • community gardens |
Also includes associated crop preparation services and harvesting activities, such as mechanical soil preparation, irrigation system construction, spraying, crop processing and retail sales in the field, not including sales sheds, which are instead defined under "Produce Stand." Does not include greenhouses or "Residential Accessory Use or Structure", which are separately defined.
Cul-de-sac. A short street or alley with only a single means of ingress and egress at one end and with a large turnaround at its other end.
Cumulative Impact. As used in CEQA, the total impact resulting from the accumulated impacts of individual projects or programs over time.
D Definitions, "D."
Day Care. Facilities that provide nonmedical care and supervision of individuals for periods of less than 24 hours. These facilities include the following, all of which are required to be licensed by the California State Department of Social Services:
1. Child Day Care Center. Commercial or nonprofit child day care facilities designed and approved to accommodate 15 or more children. Includes infant centers, preschools, sick-child centers, and school-age day care facilities. These may be operated in conjunction with a school or church facility, or as an independent land use.
2. Large Family Day Care Home. As provided by Health and Safety Code Section 1596.78, a home that regularly provides care, protection, and supervision for nine to 14 children, inclusive, including children under the age of 10 years who reside in the home, for periods of less than 24 hours per day, while the parents or guardians are away.
3. Small Family Day Care Home. As provided by Health and Safety Code Section 1596.78, a home that provides family day care for eight or fewer children, including children under the age of 10 years who reside in the home.
4. Adult Day Care Facility. A day care facility providing care and supervision for adult clients.
Dedication. The turning over by an owner or developer of private land for public use, and the acceptance of land for such use by the governmental agency having jurisdiction over the public function for which it will be used. Dedications for roads, parks, school sites, or other public uses often are made conditions for approval of a development by a city or county.
Dedication, In Lieu Of. Cash payments that may be required of an owner or developer as a substitute for a dedication of land, usually calculated in dollars per lot, and referred to as in lieu fees or in lieu contributions.
Defensible Space. (1) In fire-fighting and prevention, a 30-foot area of non-combustible surfaces separating urban and wildland areas. (2) In urban areas, open spaces, entry points, and pathways configured to provide maximum opportunities to rightful users and/or residents to defend themselves against intruders and criminal activity.
Demolition. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Density, Residential. The number of permanent residential dwelling units per gross acre of land. The residential component of a mixed use project shall comply with the density requirements of the Residential-Medium Density Zone district standards.
Density Bonus. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Department. The City of Arcata Community Development Department, referred to in this Land Use Code as the "Department."
Design Review; Design Control. The comprehensive evaluation of a development and its impact on neighboring properties and the community as a whole, from the standpoint of site and landscape design, architecture, materials, colors, lighting, and signs, in accordance with a set of adopted criteria and standards.
Detention Dam/Basin/Pond. Dams may be classified according to the broad function they serve, such as storage, diversion, or detention. Detention dams are constructed to retard flood runoff and minimize the effect of sudden floods. Detention dams fall into two main types. In one type, the water is temporarily stored, and released through an outlet structure at a rate that will not exceed the carrying capacity of the channel downstream. Often, the basins are planted with grass and used for open space or recreation in periods of dry weather. The other type, most often called a Retention Pond, allows for water to be held as long as possible and may or may not allow for the controlled release of water. In some cases, the water is allowed to seep into the permeable banks or gravel strata in the foundation. This latter type is sometimes called a Water-Spreading Dam or Dike because its main purpose is to recharge the underground water supply. Detention dams are also constructed to trap sediment. These are often called Debris Dams.
Developable Acres, Net. See "Acres, net."
Developable Land. Land that is suitable as a location for structures and that can be developed free of hazards to, and without disruption of, or significant impact on, natural resource areas.
Developer. Any person, firm, partnership, association, joint venture, corporation, or nay entity or combination of entities which seeks City approvals for all or part of a development project. Developer includes owner.
Development. On land, in or under water, the placement or erection of any solid material or structure; discharge or disposal of any dredged material or of any gaseous, liquid, solid, or thermal waste; grading, removing, dredging, mining, or extraction of any materials; change in the density or intensity of use of land, including, but not limited to, subdivision pursuant to the subdivision map act (commencing with Government Code Section 66410), and any other division of land except where the land division is brought about in connection with the purchase of such land by a public agency for public recreational use; change in the intensity of use of water, or of access thereto; construction, reconstruction, demolition, or alteration of the size of any structure, including any facility of any private, public, or municipal utility; and the removal or harvesting of major vegetation other than for agricultural purposes, kelp harvesting, and timber operations in accordance with a timber harvesting plan submitted pursuant to the provisions of the Z’berg-Nejedly Forest Practice Act of 1973 (commencing with Public Resources Code Section 4511).
Development Agreement. A contract between the City and an applicant for a development project, in compliance with the Municipal Code, and Government Code Section 65864 et seq. A development agreement is intended to provide assurance to the applicant that an approved project may proceed subject to the policies, rules, regulations, and conditions of approval applicable to the project at the time of approval, regardless of any changes to City policies, rules, and regulations after project approval. In return, the City may be assured that the applicant will provide infrastructure and/or pay fees required by a new project.
Development Fee. See "Impact Fee."
Development Rights. The right to develop land by a land owner who maintains fee-simple ownership over the land or by a party other than the owner who has obtained the rights to develop. Such rights usually are expressed in terms of density allowed under existing zoning. For example, one development right may equal one unit of housing or may equal a specific number of square feet of gross floor area in one or more specified zone districts. (See "Interest, Fee" and "Interest, Less-than-fee," and "Transfer of Development Rights [TDR].")
Development Standards. Specific requirements in a zoning ordinance or a comprehensive land use code that governs building and development as distinguished from use restrictions. For example, Development Standards would include the following site-design regulations: lot area, width, and depth; floor area ratio; site coverage; buildable area; topography development constraints; height; landscaping; parking; and signage. Also see "Standards."
Diameter of a Tree. See "Trees."
Director. The City of Arcata Community Development Director or designee of the Director.
Disaster Shelter. A facility that provides immediate and short-term housing and supplemental services for persons displaced by a major emergency or disaster. The siting of Disaster Shelters is exempt from the planning review process.
Discretionary Decision. As used in CEQA, an action taken by a governmental agency that calls for the exercise of judgment in deciding whether to approve and/or how to carry out a project.
Discretionary Permit. A City land use review and entitlement process where the review authority exercises discretion in deciding to approve or disapprove the permit. Includes Minor Use Permits, Use Permits, Variances, Design Review Approval, Planned Development Permits, and Subdivision Maps.
Diseased Tree. See "Trees."
District. An area of a city or county that has a unique character identifiable as different from surrounding areas because of distinctive architecture, streets, geographic features, culture, landmarks, activities, or land uses. Also see "Zoning District", "Historic District", and "Neighborhood Conservation Area."
Diversity. Differences among otherwise similar elements that give them unique forms and qualities; e.g., housing diversity can be achieved by differences in unit size, tenure, or cost.
Drainage Improvement. See "Grading."
Drive-through Sales or Services. A facility where food or other products may be purchased or where services may be obtained by motorists without leaving their vehicles. Examples of drive-through sales facilities include fast-food restaurants, drive-through coffee, dairy product, photo stores, pharmacies, etc. Examples of drive-through service facilities include drive-through bank teller windows, automated teller machines (ATM’s), dry cleaners/laundromats, etc., but do not include service stations or other vehicle services, which are separately defined.
Drop-in Center. A facility that provides services primarily for homeless clients, such as but not limited to hot meals, food boxes, food distribution, showers, laundry facilities, clothing, transportation, television, mail and phone contact services, support groups, and service referrals, but does not provide overnight accommodations.
Dry-lot Livestock Operation. Any 24-hour concentrated livestock operation that is usually conducted outdoors within a confined setting (i.e. below the Animal Keeping Standards as identified in Table 4-2 of this Land Use Code) for a period lasting more than six months. This type of activity does not include temporary operations for the weaning of animals or for the conditioning of animals for personal slaughter.
Due South. See "Solar Access."
Duplex. A detached building under single ownership that is designed for occupation as the residence of two families living independently of each other. See also "Multi-Family Housing" and "Second Units".
Dwelling Unit. A room or group of rooms (including sleeping, eating, cooking, and sanitation facilities, but not more than one kitchen), that constitutes an independent housekeeping unit, occupied or intended for occupancy by one household on a long-term basis.
E Definitions, "E."
Easement. A grant of one or more of the property rights by the property owner to and/or for the use by the public, a corporation or another person or entity. Usually the right to use property owned by another for specific purposes or to gain access to another property.
Easement, Conservation. A tool for acquiring open space with less than full-fee purchase, whereby a public agency buys only certain specific rights from the land owner. These may be positive rights (providing the public with the opportunity to hunt, fish, hike, or ride over the land) or they may be restrictive rights (limiting the uses to which the land owner may devote the land in the future).
Easement, Scenic. A tool that allows a public agency to use an owner’s land for scenic enhancement, such as roadside landscaping or vista preservation.
Economic Development Committee (EDC). An agency charged with seeking economic development projects and economic expansion at higher employment densities.
Elderly. Persons of age 62 and older.
Elderly Housing. See "Senior Housing".
Emergency. A sudden, unexpected occurrence demanding immediate action to prevent or mitigate loss or damage to life, health, property, or essential public services.
1. Level One Emergency. Single Incident. A level one emergency is a Minor to Moderate incident whereby local government resources are adequate and available. Example would be a natural disaster, structure fire, medical aid, vehicle accident, hazardous material, minor flooding, or a law enforcement incident. If two or more responding agencies/departments are involved with this level of incident, they will establish the Incident Command System.
2. Level Two Emergency. Widespread to Series of Incidents. A level two emergency is a Moderate to Severe emergency whereby local government resources are becoming overtaxed, and/or Operational Area mutual aid resources are being requested in support to Law Enforcement, Fire-Rescue, Public Works operations from the seven cities, special districts and/or Humboldt County departments and agencies. At this level, local government Emergency Operations Centers may be activated with minimum staffing for resource coordination in support to one or more Incident Commands. At this level, any one of the Cities Director of Emergency Services and/or Humboldt County Director of Emergency Services (Sheriff) may declare a Local Proclamation of Emergency in support to response and recovery operations.
3. Level Three Emergency. Widespread Catastrophe. A level three emergency is a Major Emergency or Disaster wherein resources in or near Humboldt County are overwhelmed and extensive local, state and/or federal mutual aid resources are required. At this level, it is usually automatic that a Local Proclamation of Emergency is declared and a Governor’s State of Emergency is requested or declared. Humboldt Operational Area (OA) EOC would be fully activated in support to the cities and field response incident commands.
Emergency Shelter. A facility that provides immediate and short-term housing and supplemental services for the homeless. Shelters come in many sizes, but an optimum size is considered to be 20 to 40 beds. Supplemental services may include food, counseling, and access to other social programs. (Also see "Transitional Housing.")
Eminent Domain. The right of a public entity to acquire private property for public use by condemnation, and the payment of just compensation.
Emission Standard. The maximum amount of pollutant legally permitted to be discharged from a single source, either mobile or stationary.
Endangered Species. A species of animal or plant is considered to be endangered when its prospects for survival and reproduction are in immediate jeopardy from one or more causes.
Environment. CEQA defines environment as "the physical conditions which exist within the area which will be affected by a proposed project, including land, air, water, mineral, flora, fauna, noise, and objects of historic or aesthetic significance."
Environmental Buffer Area (EBA). See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Environmental Impact Report (EIR). A report required pursuant to the California Environmental Quality Act which assesses all the environmental characteristics of an area, determines what effects or impacts will result if the area is altered or disturbed by a proposed action, and identifies alternatives or other measures to avoid or reduce those impacts. (See "California Environmental Quality Act.")
Environmental Impact Statement (EIS). Under the National Environmental Policy Act, a statement on the effect of development proposals and other major actions that significantly affect the environment.
Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA) definitions.
1. Artificial Wetlands. Upland that has had wetland hydrology and vegetation artificially created or planted, usually to replace wetlands that were allowed to be converted.
2. Average Low Flow Line. The elevation or point where flowing or pooled water intercepts the stream bank during the late summer season, in a normal rainfall year. This is typically evident by the change in vegetation on the stream bank.
3. Creek Zone. The area that is 25 feet outward from the top of bank, or the area bounded by the FEMA Flood Zone A line, whichever is greater, except that in no case will the creek zone on either side of a creek be wider than 100 feet from the average low flow line of the creek.
4. Coastal Creek Zone. A Creek Zone that is located within the Coastal Zone.
5. Environmental Buffer Area (EBA). An area of land separating all permitted development from adjacent sensitive habitat, streams and wetlands. The purpose of the buffer area is to prevent any degradation of the ecological functions provided by the area as a result of the development.
6. Farmed Wetland. A wetland that has been diked or drained to prevent the saturated soil conditions that would normally occur, to conduct agricultural activities (e.g., grazing), that do not require the most productive agricultural soils. These lands would typically revert to freshwater, brackish, or saltwater marsh should the dike barriers be removed. In their present state, these lands are frequently covered by shallow water during the rainy season.
7. Hydric Soils. Soils that formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to develop anaerobic conditions in the upper part.
8. Hydrophytic Vegetation. Plant life growing in water or on a substrate that is at least periodically deficient in oxygen (during a growing season) as a result of excessive water content.
9. Public Trust Lands. Lands to which California received title upon its admission to the Union and that are held by virtue of its sovereignty under the authority of the California State Lands Commission. These are lands under navigable waters including the ocean and navigable streams, and include lands formerly under water.
10. Riparian Corridor. Coastal Zone only; this term specifically applies to areas (along creeks) identified as "riparian corridors" on the Arcata Coastal Wetlands Map. Identified riparian corridors shall be regulated as wetlands where the riparian corridors extend beyond the creek zone.
11. Riparian Lands. Riparian lands are comprised of the vegetative and wildlife areas adjacent to perennial and intermittent streams. Riparian areas are delineated by the existence of plant species normally found near freshwater.
12. Stream. Any stream or waterway governed by the Arcata Creeks Management Plan, as amended, including McDaniel Slough, Gannon Slough and Butcher Slough.
13. Stream Corridor. A horizontal distance of 100 feet measured from each side of the center line of the stream, totaling a width of 200 feet; or a horizontal distance of 50 feet measured from the top of each stream or creek bank, whichever is greater. The Planning Commission may establish different horizontal measurements to match specific stream environments.
14. Stream or Creek Bank. The point where the break in slope occurs between a stream channel and surrounding topography.
15. Top of Bank. The furthest break in slope of the bank to each side of a creek. Where the top of the bank is not clearly defined by an obvious break in slope, the City Engineer shall determine the location of the top of bank.
16. Watercourse. Natural or once natural flowing (perennially or intermittently) water including rivers, streams, and creeks. Includes natural waterways that have been channelized, but does not include manmade channels, ditches, and underground drainage and sewage systems.
17. Watershed. The total area above a given point on a watercourse that contributes water to its flow; the entire region drained by a waterway or watercourse that drains into a lake, or reservoir.
18. Wetland. An area that is inundated or saturated by surface or groundwater at a frequency and duration sufficient to support, and that under normal circumstances do support, a prevalence of vegetation typically adapted for life in saturated soil conditions. Wetlands are lands where the water table is at, or near, or above the land surface long enough to promote the formation of hydric soils or to support the growth of hydrophytes, and shall also include those types of wetlands where vegetation is lacking and soil is poorly developed or absent as a result of frequent or drastic fluctuations of surface water levels, wave action, water flow, turbidity or high concentrations of salt or other substances in the substrate. These wetlands can be recognized by the presence of surface water or saturated substrate at some time during each year and their location within, or adjacent to, vegetated wetlands or deep water habitats.
19. Wetland Buffer Area. Within the Coastal Zone, the area between the edge of a wetland and the nearest paved road or the area within 250 feet of the edge of a wetland, whichever is less. The certified Coastal Wetlands Map shall be used to determine the location of the Wetland Buffer Area.
20. Wetland Delineation. The delineation by a qualified professional of the boundaries of a wetland as defined under "Wetland". For the purpose of approving development affecting a wetland, delineations shall be finalized through the :WP overlay zone review procedures.
21. Wetland Setback. An area of land adjoining a wetland, that the Commission or Zoning Administrator determines to be necessary to limit development to protect an adjoining wetland. Applies both within and outside of the Coastal Zone.
Equestrian Facility. A commercial facility for horses, donkeys, and/or mules, examples of which include horse ranches, boarding stables, riding schools and academies, horse exhibition facilities (for shows or other competitive events), and barns, stables, corrals and paddocks accessory and incidental to these uses. Does not include the simple pasturing of horses, donkeys, and/or mules, which is instead included in "Animal Keeping" as regulated by Section 9.42.050.
Equipment Rental. A service establishment that may offer a wide variety of household and business equipment, furniture, and materials for rental. Does not include construction equipment rental, which is separately defined.
Erosion and Sediment Control Plan. See "Grading."
Exaction. A contribution or payment required as an authorized development permit precondition; usually refers to mandatory dedication (or fee in lieu of dedication) requirements found in many subdivision regulations.
Excavation. See "Grading."
Expansive Soils. Soils that swell when they absorb water and shrink as they dry.
Extended Hour Retail. Any business that is open to the public between the hours of 11 p.m. and 6 a.m.
External Subsidy. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
F Definitions, "F."
Family. (1) Two or more persons related by birth, marriage, or adoption [U.S. Bureau of the Census]. (2) An individual or a group of persons living together who constitute a bona fide single-family housekeeping unit in a dwelling unit, not including a fraternity, sorority, club, or other group of persons occupying a hotel, lodging house or institution of any kind [California].
Farm Supply and Feed Store. A retail business selling supplies for use in soil preparation and maintenance, the planting and harvesting of crops, the keeping and raising of farm animals, and other operations and processes pertaining to farming and ranching. Does not include the sale, rental, or repair of farm machinery and equipment, which is instead included in the definition of "Construction and Heavy Equipment Sales and Rental."
Farmed Wetland. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Farmers Market. The temporary use of a site for the outdoor sales of food and farm produce items from vehicles, in compliance with California Food and Agriculture Code Section 1392 et seq.
Fault. A fracture in the earth’s crust forming a boundary between rock masses that have shifted.
Feasible. Capable of being accomplished in a successful manner within a reasonable period of time, taking into account economic, environmental, social and technological factors. These factors may include topographic contour, orientation, grading, slope stability, tree preservation, access to existing streets, and others.
Finding(s). The result(s) of an investigation and the evidentiary basis upon which decisions are made. Findings are used by government agents and bodies to justify action taken by the entity.
Fire Hazard Zone. An area where, due to slope, fuel, weather, or other fire-related conditions, the potential loss of life and property from a fire necessitates special fire protection measures and planning before development occurs.
Fire-resistive. Able to withstand specified temperatures for a certain period of time, such as a one-hour fire wall; not fireproof.
First-Time Home Buyer. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Fitness/Health Facility. See "Health/Fitness Facility."
Floor Area, Gross. The sum of the horizontal areas of the several floors of a building measured from the exterior face of exterior walls, or from the centerline of a wall separating two buildings, but not including any space where the floor-to-ceiling height is less than six feet.
Floor Area Ratio (FAR). The gross floor area permitted on a site divided by the total net area of the site, expressed in decimals to one or two places. For example, on a site with 10,000 net sq. ft. of land area, a Floor Area Ratio of 1.0 will allow a maximum of 10,000 gross sq. ft. of building floor area to be built. On the same site, an FAR of 1.5 would allow 15,000 sq. ft. of floor area; an FAR of 2.0 would allow 20,000 sq. ft.; and an FAR of 0.5 would allow only 5,000 sq. ft. FARs typically are applied on a parcel-by-parcel basis as opposed to an average FAR for an entire land use or zoning district. See Figure 10-1.
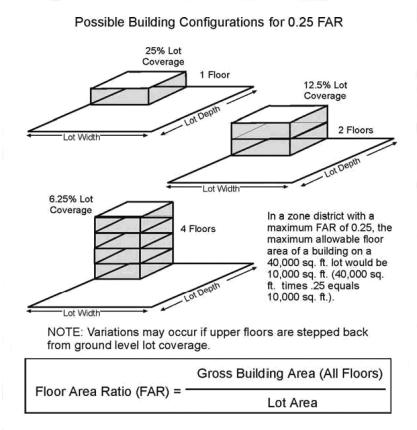
Figure 10-1 - Floor Area Ratio
Footprint; Building Footprint. The outline of a building at all of those points where it meets the ground.
Forestry. The operation and harvesting of timber tracts, tree farms, forest nurseries, and related activities including reforestation; also includes the gathering of gums, barks, sap, moss and other forest products. Does not include lumber mills, which are included under the definition of "Manufacturing - Medium Intensity."
Forest Stand. See "Trees."
Front Yard. See "Yard."
Fuel Dealer. A retail trade establishment that sells fuel oil, butane, propane and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), or alternative fuels, bottled or in bulk, to consumers.
Furniture/Fixtures Manufacturing, Cabinet Shop. Manufacturers producing: wood and metal household furniture and appliances; bedsprings and mattresses; all types of office furniture and public building furniture and partitions, shelving, lockers and store furniture; and miscellaneous drapery hardware, window blinds and shades. Includes furniture re-upholstering businesses, wood and cabinet shops, but not sawmills or planing mills, which are instead included under "Manufacturing - Heavy."
Furniture, Furnishings and Appliance Store. A store that primarily sells the following products and related services, that may also provide incidental repair services:
|
• computers and computer equipment • draperies • floor coverings • furniture • glass and chinaware • home appliances • home furnishings • home sound systems • interior decorating materials and services |
|
• large musical instruments • lawn furniture • movable spas and hot tubs • office furniture • other household electrical and gas appliances • outdoor furniture • refrigerators • stoves • televisions |
G Definitions, "G."
Garage, or Carport. Parking space and shelter for automobiles or other vehicles, where the size of the parking space complies with the provisions of Chapter 9.36 (Parking and Loading).
1. A garage is an attached or detached accessory structure with a door, enclosed on at least three sides.
2. A carport is an attached or detached accessory structure enclosed on no more than two sides.
A garage or carport complies with the requirements of this Land Use Code for covered parking spaces.
Gas Station. "See Service Station."
General Plan. The City of Arcata General Plan, including all its elements and all amendments thereto, as adopted by the City Council in compliance with Government Code Section 65300 et seq., and referred to in the Land Use Code as the General Plan. The General Plan serves as the constitution of a community; the General Plan expresses the goals, policies, and direction to provide the basis for rational decisions regarding the long-term development of a community.
General Retail. Stores and shops selling many lines of merchandise. Examples of these stores and lines of merchandise include:
|
• antique stores • art galleries, retail • art supplies, including framing services • auction rooms • bicycles • books, magazines, and newspapers • cameras and photographic supplies • clothing, shoes, and accessories • collectibles (cards, coins, comics, stamps, etc.) • department stores • drug stores and pharmacies • dry goods • fabrics and sewing supplies • florists and houseplant stores (indoor sales only - outdoor sales are "Building and Landscape Materials Sales") |
|
• groceries, food products • hobby materials • jewelry • luggage and leather goods • musical instruments, parts and accessories • orthopedic supplies • religious goods • small wares • specialty shops • sporting goods and equipment • stationery • toys and games • variety stores |
Geologic Review. The analysis of geologic hazards, including all potential seismic hazards, surface ruptures, liquefaction, landslides, mudslides, and the potential for erosion and sedimentation.
Golf Course, Country Club. Golf courses, and accessory facilities and uses including: clubhouses with bar and restaurant, locker and shower facilities; driving ranges; "pro shops" for on-site sales of golfing equipment; and golf cart storage and sales facilities.
Grade. The ground surface immediately adjacent to the exterior base of a structure, typically used as the basis for measurement of the height of the structure.
Grading. The following terms and phrases are defined for the purposes of Chapter 9.64 (Grading, Erosion, and Sediment Control).
1. Bench. A relatively level step excavated into earth material on which fill is to be placed.
2. BMP. Best Management Practices, as defined by the State Water Resources Control Board’s Best Management Practices Construction Handbook.
3. Channel or Drainage Way. A natural or artificial open watercourse with definite bed and banks which periodically or continuously contains moving water or forms a connecting link between two bodies of water.
4. Discharge. The outflow rate of surface water.
5. Drainage Improvement. Any element in a drainage system which is made or improved by a human.
6. Erosion. (1) The loosening and transportation of rock and soil debris by wind, rain, or running water. (2) The gradual wearing away of the upper layers of earth.
7. Erosion and Sediment Control Plan. A plan that fully indicates necessary land treatment and structural measures, including a schedule of timing for their installation, which will effectively minimize soil erosion and sediment yield. Such measures shall be in accordance with standards shown in the City of Arcata Erosion and Sediment Control Handbook.
8. Excavation. The physical removal of earth material.
9. Fill. The deposit of earth material caused or placed by artificial means.
10. Grading. Any excavating, filling, or any combination thereof.
11. Land Disturbing Activity. Any land change which may result in soil erosion from water, wind and the movement of sediments onto adjacent properties. Such activities include but are not limited to clearing, grading, excavating, transporting and filling of land.
12. Mulch. A natural or artificial layer of material placed on exposed earth to provide more desirable moisture and temperature relationships for plant growth. It is also used to control the occurrence of unwanted vegetation.
13. Natural or Existing Grade. The contour of the ground surface before grading.
14. Sediment. Solid material, both mineral and organic, that is in suspension, is being transported, or has been moved from its site of origin by air, water, or gravity.
15. Sediment Detention Basin. A sediment detention basin is a reservoir which retains flows sufficiently to cause deposition of transported sediment.
16. Short Form [Erosion and Sediment Control Plan]. A simplified form, issued by the Building Official, for erosion and sediment control plans for certain qualifying minor grading projects.
17. Storm Water Runoff. The waters which result from rainfall flowing over the surface of the ground.
18. Swale. A low lying stretch of land which gathers or carries surface water runoff.
19. Terrace. A relatively level step constructed in the face of a graded slope surface for drainage and maintenance purposes.
Greenbelt. A strip of land, in or adjacent to a city, that contains open space such as wetlands, natural resource lands, parks, farms, or vacant land.
Greenfield. Undeveloped or even developed lands that do not have previously identified or suspected environmental contamination.
Greenhouse or Nursery Structure. A commercial or hobby agricultural structure for the production of plants and other nursery products, grown under cover either in containers or in the soil on the site (soil dependent). The outdoor production of ornamental plants in the soil on the site is instead included under "Crop Production, Horticulture, Orchard, Vineyard." The sale of house plants or other nursery products entirely within a building is also included under "General Retail."
Greenwaste. Means waste tree trimmings, brush, lawn clippings, or untreated wood.
Grocery Store. A retail business where the majority of the floor area open to the public is occupied by food products packaged for preparation and consumption away from the store.
Ground Disturbing Activity. Any activity associated with the cultivation or tillage of soil for agricultural, tree planting, crop production, home gardening, or similar activities that are exempt from other activities that are associated with Grading or Land Disturbing Activities.
Ground Failure. Ground movement or rupture caused by strong shaking during an earthquake. Includes landslide, lateral spreading, liquefaction, and subsidence.
Ground Shaking. Ground movement resulting from the transmission of seismic waves during an earthquake.
Groundwater. Water under the earth’s surface, often confined to aquifers capable of supplying wells and springs.
Groundwater Recharge. The natural process of infiltration and percolation of rainwater from land areas or streams through permeable soils into water-holding rocks that provide underground storage ("aquifers").
Group Quarters. A residential living arrangement in which more than six unrelated persons share living quarters and cooking facilities. Group quarters may include, but are not limited to, any of the following: drug/alcohol rehabilitation centers, halfway houses, housing for handicapped or disabled persons, foster care center, or a care facility for 24-hour medical care of persons in need of personal services, supervision, or assistance for sustaining the activities of daily living or for the protection of the individual.
Growth Management. The use by a community of a wide range of techniques in combination to determine the amount, type, and rate of development desired by the community and to channel that growth into designated areas. Growth management policies can be implemented through growth rates, zoning, capital improvement programs, public facilities ordinances, urban limit lines, standards for levels of service, and other programs. (See "Congestion Management Plan.")
Guest House. A detached structure accessory to a single-family dwelling, accommodating living/sleeping quarters, but without kitchen or cooking facilities.
H Definitions, "H."
Habitable Space. Space within a dwelling unit for living, sleeping, eating, or cooking.
Habitat. The physical location or type of environment in which an organism or biological population lives or occurs.
Handicapped. A person determined to have a physical impairment or mental disorder expected to be of long or indefinite duration. Many such impairments or disorders are of such a nature that a person’s ability to live independently can be improved by appropriate housing conditions.
Hazardous Material. Any substance that, because of its quantity, concentration, or physical or chemical characteristics, poses a significant present or potential hazard to human health and safety or to the environment if released into the workplace or the environment. The term includes, but is not limited to, hazardous substances and hazardous wastes.
Hazardous Tree. See "Trees."
Health/Fitness Facility. A fitness center, gymnasium, health and athletic club, which may include any of the following: sauna, spa or hot tub facilities; indoor tennis, handball, racquetball, archery and shooting ranges and other indoor sports activities. Does not include sex oriented businesses.
Height. See Section 9.30.040 (Height Limits and Exceptions).
Historical Resource Preservation definitions:
1. Adaptive Use/Reuse. The process of converting a building to a use other than that for which it was designed.
2. Alteration of a Historic Resource. Any exterior change or modification, through public or private action, of any historical resource, whether formally designated or determined eligible for listing which involves exterior changes to or modification of a structure, its surface texture, or its architectural details that includes: new construction; partial demolition; relocation of structures onto, off of, or within a designated property or parcel located in a Neighborhood Conservation Area or other changes to the site affecting the significant historical or architectural features of the property.
3. Archeological Site. A bounded area of a resource containing archeological deposits or features that is defined in part by the character and location of such deposits or features.
4. Demolition. The destruction or removal of a structure, or parts of a structure that is so extensive that the historic character of a designated historic resource is completely removed and cannot be repaired or replaced.
5. Historic Conservation Easement. A less than fee simple interest in real property recorded as a deed restriction which is designed to protect the historical, cultural, archaeological, or ecological characteristics of a property.
6. Historic Context. An organizing structure for interpreting history that groups information about historical resources sharing a common theme, geographical area, or chronology. The development of "historic context" is a foundation for decisions regarding the planning, identification, evaluation, registration, and treatment of historical resources based upon comparative historic significance.
7. Historic District or Area. A geographically definable area of urban or rural character, possessing a significant concentration or continuity of site, building, structures or objects unified by past events or aesthetically by plan or physical development.
8. Historic Fabric. (1) With regard to an historic building, "historic fabric" means the particular materials, ornamentation, and architectural features which are consistent with the historic character of the building. (2) With regard to an historic district, "historic fabric" means all sites, buildings, structures, features, objects, landscaping, street elements, and related design components of the district which are consistent with the historic character of the district. (3) With regard to an archeological district, "historic fabric" means sites, standing structures or buildings, historic landscape (land disturbance such as grading or construction), features (remnants of walls), and objects (artifacts) which are consistent with the historic character of the district.
9. Historic Integrity. The ability of a resource to convey its historical significance.
10. Historical Preservation. The preservation of historically significant structures and neighborhoods until such time as, and in order to facilitate, restoration and rehabilitation of the building(s) to a former condition.
11. Historical Resource. Any site, building, structure, area or place, man-made or natural, which meets the CEQA criteria for an historic resource as determined by a professional historian, architectural historian, cultural resources consultant, heritage resources consultant, archaeologist or qualified professional from a related field.
12. Historical Resources Inventory. A set of data, such as a list of historical resources, generated through a Historical Resources Survey.
13. Historical Resources Survey. The process of systematically identifying, researching, photographing, and documenting historical resources within a defined geographic area.
14. Landmark. (1) A building, site, object, structure, or significant tree, having historical, architectural, social, or cultural significance and marked for preservation by the local, state, or federal government. (2) A visually prominent or outstanding structure or natural feature that functions as a point of orientation or identification.
15. Landscape, Cultural. A geographic area that (1) has been used, shaped, or modified by human activity, occupation, intervention; or (2) possesses significant value in the belief system of a culture or society.
16. Local government. A public agency with land-use control authority over a designated historical resource. Local governments may include special district, tribal, city, or county governments.
17. Local Register of Historic Places. A landmark list established by the City of Arcata of locally, regionally, and/or nationally significant properties and districts within the City that have been formally designated.
18. National Historic Preservation Act of 1966 (NHPA). (16 U.S.C. 470 (1966) (amended)). Established the National Register of Historic Places. Created a partnership between federal, state, and local agencies to extend the national historic preservation programs to properties of state and local significance.
19. National Register of Historic Places. The official list, established by the National Historic Preservation Act, of sites, districts, buildings, structures, and objects significant in the nation’s history or whose artistic or architectural value is unique.
20. Neighborhood Conservation Area. An area within the City designated by the General Plan to be historically noteworthy where review is conducted to assure that new construction, modifications or alterations of noteworthy structures, and significant changes to other structures are harmonious with the existing character of the neighborhood.
21. Non-contributing Structure or Building. A building or structure located within a designated historic district or Neighborhood Conservation Area that does not possess the qualifications or characteristics of an eligible building due to such factors as age or alteration, but has been included within the district because of its impact on the geographic integrity and overall character of the district.
22. Noteworthy Structures. Those structures that may be eligible for Historic Landmark designation and may not have complete documentation as to their historical or architectural merit.
23. Office of Historic Preservation (OHP). The California State Office of Historic Preservation in Sacramento.
24. Preservation. The act or process of applying measures to sustain the existing form, integrity and material of an historic resource. It may include initial stabilization work, where necessary, as well as ongoing maintenance of the historic building materials.
25. Reconstruction. The act or process of reproducing by new construction the exact form and detail of a vanished building, structure or object, or a part thereof, as it appeared at a specified period of time.
26. Recordation, County. Section 27288.2 of the Government Code and Section 5029 of the Public Resources Code require the County Recorder to record a certified resolution of historical resources designation containing the name of the current property owner, the historical resources registration program, the designating entity, the specific historical resources designation, and a legal description of the property.
27. Regional Information Center. An Information Center of the California Historical Resources Information System, under contract to the Office of Historic Preservation, which receives, manages, and provides information on historical and archeological resources. "An Information Center" may also provide training or technical assistance on a fee-for-service basis.
28. Rehabilitation. The act or process of making a compatible use for a property through repair, alterations and additions while preserving those portions or features which convey its historical, cultural or architectural values.
29. Remodeling. Making over or rebuilding all or part of an historic structure in a way that does not necessarily preserve its historical, architectural, and cultural features and character.
30. Restoration. The act or process of accurately recovering the form and details of a property and its setting as it appeared at a particular period of time by means of the removal of later work or by the replacement of missing earlier work.
31. Secretary of the Interior’s Standards. The Secretary of the Interior’s Standards for the Treatment of Historic Properties published by the U.S. Department of the Interior that provide the standards and guidelines for appropriate rehabilitation, restoration, preservation and new construction to historic buildings and within historic districts.
32. Significance. A term ascribed to buildings, sites, objects, or districts that possess exceptional value or quality for illustrating or interpreting the cultural heritage of the community when evaluated in relation to other properties and property types within a specific historic theme, period, and geographical setting. A principal test of significance for historic property is "integrity."
33. Significant Architectural Features. The architectural elements embodying style, design, general arrangement and components of all of the outside surfaces of a building, structure or object, including but not limited to the type of building materials and the type and style of all windows, doors, lights, signs and other fixtures appurtenant to such building, structure or object that have special historical, architectural, cultural or aesthetic interest or values and have been designated as such under a local, state or federal historic property registration program.
34. Stabilization. The act or process of applying measures designed to reestablish a weather resistant enclosure or the structural stability of an unsafe or deteriorated property while maintaining the essential form as it exists at present.
35. State Historical Building Code (SHBC). The State Historical Building Code is contained in Part 8 of Title 24 (State Building Standards Code) and applies to all qualified historical structures, districts, and sites designated under federal, state, or local authority. It provides alternatives to the Uniform Building Code in cases consistent with building regulations for the rehabilitation, preservation, restoration, or relocation of qualified historic structures designated as historic buildings.
Home Occupation. The conduct of a business within a dwelling unit or residential site, employing only the occupants of the dwelling (unless waived through the Minor Use Permit process), with the business activity being subordinate to the residential use of the property.
Hotel or Motel. See "Lodging."
Household. All those persons-related or unrelated, who occupy a single housing unit (see "Family").
Household Pets. The keeping/raising of birds, cats, dogs, or other common household animals, as determined by the Director, accessory to a residential use.
Households, Number of. The count of all year-round housing units occupied by one or more persons. The concept of household is important because the formation of new households generates the demand for housing. Each new household formed creates the need for one additional housing unit or requires that one existing housing unit be shared by two households. Thus, household formation can continue to take place even without an increase in population, thereby increasing the demand for housing.
Housing Trust Fund. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Housing Unit. The place of permanent or customary abode of a person or family. A housing unit may be a single-family dwelling, a multi-family dwelling, a condominium, a modular home, a mobile home, a cooperative, or any other residential unit considered real property under State law. A housing unit has, at least, cooking facilities, a bathroom, and a place to sleep. It also is a dwelling that cannot be moved without substantial damage or unreasonable cost. (See "Dwelling Unit," "Family," and "Household.")
Hydric Soils. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Hydrophytic. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
I Definitions, "I."
Impact. The effect of any direct man-made actions or indirect repercussions of man-made actions on existing physical, social, or economic conditions.
Impact Fee. A fee, also called a development fee, levied by a city, county, or other public agency on the developer of a project as compensation for otherwise-unmitigated impacts the project will produce. Sections 66000, et seq., specify that development fees shall not exceed the estimated reasonable cost of providing the service for which the fee is charged. To lawfully impose a development fee, the public agency must verify its method of calculation and document proper restrictions on use of the fund.
Impervious Surface. Surface through which water cannot penetrate, such as roof, road, sidewalk, and paved parking lot. The amount of impervious surface increases with development and establishes the need for drainage facilities to carry the increased runoff.
Implementation Measure. Actions, procedures, programs, or techniques that carry out policies.
Incineration. The burning of refuse at high temperatures to reduce the volume of waste.
Inclusionary Housing Plan. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Inclusionary Incentives. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Inclusionary Unit. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Inclusionary Zoning. Provisions established by a public agency to require that a specific percentage of housing units in a project or development remain affordable to very low, low, and moderate-income households for a specified period.
Incubator Space. Retail or industrial space that is affordable to new, low-margin businesses.
Independent Living Center/Senior Apartment. See "Residential Care Facility for the Elderly (RCFE)."
Industrial. The manufacture, production, and processing of consumer goods. Industrial is often divided into "heavy industrial" uses, such as construction yards, quarrying, and factories; "moderate impact manufacturing", and "light industrial" uses, such as research and development and less intensive warehousing and manufacturing.
Industrial Research and Development (R&D). A facility for scientific research, and the design, development and testing of electrical, electronic, magnetic, optical and computer and telecommunications components in advance of product manufacturing, and the assembly of related products from parts produced off-site, where the manufacturing activity is secondary to the research and development activities. Includes pharmaceutical, chemical and biotechnology research and development. Does not include soils and other materials testing laboratories (see "Laboratory"), or medical laboratories (see "Medical Service - Clinic, Laboratory, Urgent Care").
Industrial Zoning District. Any of the industrial zoning districts established by Section 9.12.020 (Zoning Map and Zoning Districts).
Infill Development. Development, redevelopment or reuse of land that is either underutilized, brownfield or vacant, but substantially surrounded by existing urban development. In all instances, infill development occurs on sites that already have sufficient City services immediately available. Infill development may include new residential units on upper floors of commercial structures, development of second units on residential lots, and new or expansion of existing residential and commercial structures and uses consistent with the provisions of the applicable land use and zoning designations.
Infrastructure. Public services and facilities, such as sewage-disposal systems, water-supply systems, other utility systems, and roads.
Initial Owner. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
In Lieu Fee. See "Dedication, in lieu of."
Intensification of Use. A change in the use of a structure or site, where the new use is required by this Land Use Code to have more off-street parking spaces than the former use; or a change in the operating characteristics of a use (for example, hours of operation), which generates more activity on the site.
Intensity, Building. For residential uses, the actual number or the allowable range of dwelling units per net or gross acre. For non-residential uses, the actual or the maximum permitted floor area ratios (FARs).
Interpretive Center. A facility where information oriented to students and the general public is provided about natural resources on the site or in the vicinity of the facility. May include areas for displays and presentations, meetings, research, facility management, and overnight camping related to the resources and/or areas that are the subject of the center.
J Definitions, "J."
No specialized terms beginning with the letter "J" are defined at this time.
K Definitions, "K."
Kennel, Animal Boarding. A commercial facility for the grooming, keeping, boarding or maintaining of five or more dogs (four months of age or older), or five or more cats except for dogs or cats for sale in pet shops, or patients in animal hospitals. See also "Veterinary Clinic, Animal Hospital".
Kitchen. A room or space within a building used or intended to be used for the cooking or preparation of food.
L Definitions, "L."
Laboratory - Medical, Analytical, Testing. A facility for testing, analysis, and/or research. Examples of this use include medical labs, soils and materials testing labs, and forensic labs.
Land Banking. The purchase of land by a local government for use or resale at a later date. "Banked lands" have been used for development of low- and moderate-income housing, expansion of parks, and development of industrial and commercial centers. Federal rail-banking law allows railroads to bank unused rail corridors for future rail use while allowing interim use as trails.
Land Disturbing Activity. See "Grading."
Landmark. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Landmark Trees. See "Trees."
Landscape, Cultural. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Landslide. Downslope movement of soil and/or rock, which typically occurs during an earthquake or following heavy rainfall.
Land Use. The purpose for which a lot or structure is or may be leased, occupied, maintained, arranged, designed, intended, constructed, erected, moved, altered, and/or enlarged in accordance with the City zoning ordinance and General Plan land use designations.
Land Use Code (LUC). The City of Arcata Land Use Code, Title 9 of the Arcata Municipal Code, referred to within this document as the comprehensive land use code or LUC. The Land Use Code is the implementation tool of the General Plan as it prescribes zoning, mapping, specific development standards, and other regulations to carry out the goals, policies, and direction of the General Plan.
Land Use Permit. Authority granted by the City to use a specified site for a particular purpose. "Land Use Permit" includes Use Permits, Minor Use Permits, Variances, Coastal Permits, Planned Development Permits, Design Review and Zoning Clearances, as established by Article 7 (Planning Permit Procedures).
Landscaping Standards. The following terms are defined for the purposes of Chapters 9.34 (Landscape Standards).
1. Landscaped area. The parcel area less building footprints, driveway, parking areas, paved walks and patios, and undeveloped open space of designated natural areas. Project landscaped area includes all areas under irrigation, water features, and hardscape other than those noted above.
2. Microclimate. A section of a landscaped site with unique climatic conditions that affect the amount of water plants within the area use (e.g., courtyards, tree understory areas, and median islands).
3. Native species. A species that existed in California prior to European contact.
4. Overspray. Water which is discharged from an overhead irrigation system outside the desired planting area, especially water which wets adjacent hard surfaces (e.g., patios, sidewalks, and streets).
5. Porous mulch. A loose material applied to the soil surface to reduce evaporation and retard weed growth (e.g., compost, decomposed granite, straw, wood chips).
6. Runoff. Water which is not absorbed by the soil to which it is applied and runs off onto other areas. Runoff usually occurs when water is applied at a rate greater than the infiltration rate of the soil, and is especially problematic on slopes and on heavy clay soils.
7. Water feature. Ornamental or functional body of water (e.g., a fountain, pool, or pond).
Large Family Day Care Home. See "Day Care."
Lateral Spreading. Lateral movement of soil, often as a result of liquefaction during an earthquake.
Laundry, Dry Cleaning Plant. A service establishment engaged primarily in high volume laundry and garment services, including: carpet and upholstery cleaners; diaper services; dry cleaning and garment pressing; commercial laundries; linen supply. These facilities may include accessory customer pick-up facilities. These facilities do not include coin-operated laundries or dry cleaning pick-up stores without dry cleaning equipment; see "Personal Services."
Lease. A contractual agreement by which an owner of real property (the lessor) gives the right of possession to another (a lessee) for a specified period of time (term) and for a specified consideration (rent).
Leasehold Interest. (1) The interest that the lessee has in the value of the lease itself in condemnation award determination. (2) The difference between the total remaining rent under the lease and the rent the lessee would currently pay for similar space for the same time period.
Legislative Entitlement. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Level of Service (LOS) Standard. A standard used by government agencies to measure the quality or effectiveness of a municipal service, such as police, fire, or library, or the performance of a facility, such as a street or highway.
Library, Museum. Public or quasi-public facilities, examples of which include: aquariums, arboretums, art galleries and exhibitions, botanical gardens, historic sites and exhibits, libraries, museums, planetariums, and zoos. May also include accessory retail uses such as a gift/book shop, restaurant, etc.
Life Care Facility. See "Residential Care Facility for the Elderly (RCFE)."
Liquefaction. The transformation of loose, wet soil from a solid to a liquid state, often as a result of ground shaking during an earthquake.
Live/Work Unit. An integrated housing unit and working space, occupied and utilized by a single household in a structure, either single-family or multi-family, that has been designed or structurally modified to accommodate joint residential occupancy and work activity, and which includes:
1. Complete kitchen space and sanitary facilities in compliance with the Building Code; and
2. Working space reserved for and regularly used by one or more occupants of the unit.
Local Agency Formation Commission (LAFCO). A five- or seven-member commission within each county that reviews and evaluates all proposals for formation of special districts, incorporation of cities, annexation to special districts or cities, consolidation of districts, and merger of districts with cities. Each county’s LAFCO is empowered to approve, disapprove, or conditionally approve such proposals. The LAFCO members generally include two county supervisors, two city council members, and one member representing the general public. Some LAFCOs include two representatives of special districts.
Local Coastal Program (LCP). A combination of a local government’s land use plans, zoning ordinances, zoning district maps, and (within sensitive coastal resources areas) other implementing actions that together meet the local requirements of, and implement the provisions and policies of, the California Coastal Act of 1976.
Local Coastal Program Land Use Plan. The relevant portion of a local government general plan or coastal element that details type, location, and intensity of land use, applicable resource protection and development policies, and, where necessary, implementation actions.
Local government. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Local Register of Historic Places. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
1. Bed and Breakfast Inn (B&B). A residential structure with one or more bedrooms rented for overnight lodging, where meals may be provided subject to applicable Environmental Health Department regulations. Does not include room rental, which is separately defined (see "Rooming or Boarding House").
2. Campground. A site used or intended for use for temporary occupancy by persons traveling by automobile or otherwise, which may include individual campsites, but where utility hookups for recreational vehicles are not provided.
3. Hostel. The provision of overnight lodging in dormitories or shared rooms, with shared bathroom facilities.
4. Hotel or Motel. A facility with guest rooms or suites, with or without kitchen facilities, rented to the general public for transient lodging. Hotels typically include a variety of services in addition to lodging; for example, restaurants, meeting facilities, personal services, etc. Also includes accessory guest facilities such as swimming pools, tennis courts, indoor athletic facilities, accessory retail uses, etc.
5. Recreational Vehicle (RV) Park. A site where one or more lots are used, or are intended to be used, by persons with recreational vehicles or tents. Recreational vehicle parks may include public restrooms, water, sewer, and electric hookups to each lot and are intended as a higher density, more intensively developed use than campgrounds. May include accessory retail uses where they are clearly incidental and intended to serve RV park patrons only.
6. Vacation Rental. Rental of primary residences and secondary units on a seasonal or short term basis.
Lot Area. Gross lot area is the total area included within the lot lines of a lot, exclusive of adjacent dedicated street rights of way. Net lot area is the gross area of the lot, exclusive of easements for streets or driveways that are not for the exclusive use of the lot on which the easement is located.
Lot or Parcel. A recorded lot or parcel of real property under single ownership, lawfully created as required by applicable Subdivision Map Act and City ordinance requirements, including this Land Use Code. Types of lots include the following. See Figure 10-2 (Lot Types).
1. Corner Lot. A lot located at the intersection of two or more streets.
2. Flag Lot. A lot having access from the building site to a public street by means of private right-of-way strip that is owned in fee.
3. Interior Lot. A lot abutting only one street.
4. Key Lot. An interior lot, the front of which adjoins the side property line of a corner lot.
5. Reverse Corner Lot. A corner lot, the rear of which abuts a key lot.
6. Double Frontage Lot. A lot with frontage on two generally parallel streets.
Figure 10-2 - Lot Types
Lot Coverage. See "Site Coverage."
Lot Depth. The average linear distance between the front and the rear lot lines or the intersection of the two side lot lines if there is no rear line. See Figure 10-3 (Lot Features). The Director shall determine lot depth for parcels of irregular configuration.
Lot Frontage. The boundary of a lot adjacent to a public street right-of-way.
Lot Line or Property Line. Any recorded boundary of a lot. Types of lot lines are as follows (see Figure 10-3 (Lot Features)):
1. Front Lot Line. On an interior lot, the property line separating the parcel from the street. The front lot line on a corner lot is the line with the shortest frontage. (If the street-fronting lot lines of a corner lot are equal in length, the front lot line shall be determined by the Director.) On a double-frontage lot, both lot lines are front lot lines and the lot is considered to have no rear lot line.
2. Interior Lot Line. Any lot line not abutting a street.
3. Rear Lot Line. A property line that does not intersect the front lot line, which is most distant from and most closely parallel to the front lot line.
4. Side Lot Line. Any lot line that is not a front or rear lot line.
Figure 10-3 - Lot Features
Lot Width. The horizontal distance between the side lot lines, measured at right angles to the lot depth at a point midway between the front and rear lot lines. See Figure 10-2 (Lot Features). The Director shall determine lot width for parcels of irregular shape.
Low Income Household. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Low-income Housing Tax Credits. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
M Definitions, "M."
Maintenance Service, Client Site Services. Base facilities for various businesses that provide services on the premises of their clients. Includes gardening, janitorial, pest control, water and smoke damage recovery, and similar services; and appliance, computer, electronics, elevator, equipment, HVAC, instrument, plumbing, and other maintenance and repair services not operating from a retail establishment that sells the products being maintained or repaired. When these services operate from a retail establishment that sells the products being maintained or repaired, they are instead considered part of the retail use.
Manufactured Home. See "Mobile Home."
Manufactured Housing. Residential structures that are constructed entirely in the factory, and which since June 15, 1976, have been regulated by the federal Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards Act of 1974 under the administration of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). (See "Mobile Home" and "Modular Unit.")
Manufacturing/Processing - High Impact. A facility accommodating manufacturing processes that involve and/or produce basic metals, building materials, chemicals, fabricated metals, paper products, machinery, textiles, and/or transportation equipment, where the intensity and/or scale of operations may cause significant impacts on surrounding land uses or the community. Heavy manufacturing uses are not allowed within the City of Arcata except where limited varieties are included under the definition of "Manufacturing/Processing - High Impact." Examples of heavy manufacturing uses include the following.
1. Chemical Product Manufacturing. An establishment that produces or uses basic chemicals, and other establishments creating products predominantly by chemical processes. Examples of these products include: basic chemicals, including acids, alkalis, salts, and organic chemicals; chemical products to be used in further manufacture, including synthetic fibers, plastic materials, dry colors, and pigments; and finished chemical products to be used for ultimate consumption, including drugs/pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and soaps; or to be used as materials or supplies in other industries including paints, fertilizers, and explosives. Also includes sales and transportation establishments handling the chemicals described above, except as part of retail trade.
2. Concrete, Gypsum, and Plaster Product Manufacturing. An establishment that produces bulk concrete, concrete building block, brick, and/or other types of precast and prefabricated concrete products. Also includes ready-mix concrete batch plants, lime manufacturing, and the manufacture of gypsum products, including plasterboard. A retail ready-mix concrete operation as an incidental use in conjunction with a building materials outlet is defined under "Building and Landscape Materials Sales."
3. Glass Product Manufacturing. An establishment that manufactures glass and/or glass products by melting silica sand or cullet, including the production of flat glass and other glass products that are pressed, blown, or shaped from glass produced in the same establishment. Artisan and craftsman type operations of a larger scale than home occupations are instead included under ("Manufacturing/Processing - Low Impact - Handcraft Industries and Small-Scale Manufacturing").
4. Paving and Roofing Materials Manufacturing. The manufacture of various common paving and petroleum-based roofing materials, including bulk asphalt, paving blocks made of asphalt, creosote wood, and various compositions of asphalt and tar. Does not include the manufacture of wood roofing materials (shingles, shakes, etc.) ("Lumber and Wood Product Manufacturing").
Revised by Ord. #1382 - Effective 12/22/08
5. Petroleum Refining and Related Industries. Industrial plants for purifying petroleum, and the compounding of lubricating oils and greases from purchased materials. Also includes oil or gas processing facilities, liquefied natural gas (LNG) facilities, the manufacture of petroleum coke and fuel briquettes, tank farms, and terminal facilities for pipelines. Does not include petroleum pipeline surge tanks and pump stations ("Public Utility Facilities"), or petroleum product distributors ("Petroleum Product Storage and Distribution").
6. Plastics, other Synthetics, and Rubber Product Manufacturing. The manufacture of rubber products including: tires, rubber footwear, mechanical rubber goods, heels and soles, flooring, and other rubber products from natural, synthetic, or reclaimed rubber. Also includes establishments engaged primarily in manufacturing tires; products from recycled or reclaimed plastics or styrofoam; molding primary plastics for other manufacturers, manufacturing miscellaneous finished plastics products, fiberglass manufacturing, and fiberglass application services. Does not include establishments engaged primarily in recapping and retreading automobile tires ("Vehicle Services - Major Repair/Body Work").
7. Primary Metal Industries. An establishment engaged in: the smelting and refining of ferrous and nonferrous metals from ore, pig, or scrap; the rolling, drawing, and alloying of metals; the manufacture of castings, forgings, stampings, extrusions, and other basic metal products; and the manufacturing of nails, spikes, and insulated wire and cable. Also includes merchant blast furnaces and by-product or beehive coke ovens.
8. Pulp and Pulp Product Manufacturing. An establishment that manufactures pulp, paper, or paperboard. Includes pulp, paper, and paperboard mills. Does not include establishments primarily engaged in converting paper or paperboard without manufacturing the paper or paperboard, including envelope manufacturing, converted paper products, paper coating and glazing, paper bags, assembly of paperboard boxes, wallpaper (Manufacturing/Processing - Low Impact Paper Product Manufacturing).
9. Textile and Leather Product Manufacturing. An establishment that converts basic fibers (natural or synthetic) into a product, including yarn or fabric, that can be further manufactured into usable items ("Manufacturing/Processing - Low Impact - Clothing and Fabric Product Manufacturing"), and industries that transform hides into leather by tanning or curing. Includes:
|
• coating, waterproofing, or otherwise treating fabric • dressed and dyed furs • dyeing and finishing fiber, yarn, fabric, and knit apparel • leather-tanned, curried, and finished • manufacture of knit apparel and other finished products from yarn • manufacture of felt goods, lace goods, non-woven fabrics and miscellaneous textiles |
|
• manufacturing of woven fabric, carpets, fabric and rugs from yarn • preparation of fiber and subsequent manufacturing of yarn, threads, braids, knit apparel twine cordage • scouring and combing plants • upholstery manufacturing • yarn and thread mills |
10. Lumber and Wood Product Manufacturing. Large scale (one acre or more) manufacturing, processing, storage, and sales involving the milling of forest products to produce rough and finished lumber and other wood materials for use in other manufacturing, craft, or construction processes. Includes the following processes and products:
|
• boxes and cooperages • containers, pallets and skids • manufactured and modular homes • matches (wood) • milling operations |
|
• trusses and structural beams • turning and shaping of wood products • wholesaling of basic wood products • wood product assembly |
Does not include craft-type shops ("Handcraft Industries and Small-Scale Manufacturing"); other wood and cabinet shops ("Furniture and Fixture Manufacturing, Cabinet Shops"); or the entirely indoor retail sale of building materials, construction tools and equipment ("Building and Landscape Materials Sales").
Manufacturing/Processing - Moderate Impact. A facility accommodating manufacturing processes that involve and/or produce building materials, fabricated metal products, machinery, and/or transportation equipment, where the intensity and/or scale of operations is greater than those classified under "Manufacturing/Processing - Low Impact," but where impacts on surrounding land uses or the community can typically be mitigated to acceptable levels. Examples of moderate impact manufacturing uses include the following.
1. Lumber and Wood Product Manufacturing. Small scale (40,000 square feet or less) manufacturing, processing, storage, and sales involving the milling of forest products to produce rough and finished lumber and other wood materials for use in other manufacturing, craft, or construction processes. Includes the following processes and products:
|
• boxes and cooperages • containers, pallets and skids • manufactured and modular homes • matches (wood) • milling operations |
|
• trusses and structural beams • turning and shaping of wood products • wholesaling of basic wood products • wood product assembly |
Does not include craft-type shops ("Handcraft Industries and Small-Scale Manufacturing"); other wood and cabinet shops ("Furniture and Fixture Manufacturing, Cabinet Shops"); or the entirely indoor retail sale of building materials, construction tools and equipment ("Building and Landscape Materials Sales").
2. Machinery Manufacturing. An establishment that makes or processes raw materials into finished machines or parts for machines. Does not include the manufacture of electronics, equipment, or appliances ("Electronics, Equipment, and Appliance Manufacturing").
3. Metal Products Fabrication, Machine and Welding Shops. An establishment engaged in the production and/or assembly of metal parts, including the production of metal cabinets and enclosures, cans and shipping containers, doors and gates, duct work, forgings and stampings, hardware and tools, plumbing fixtures and products, tanks, towers, and similar products. Examples of these uses include:
|
• blacksmith and welding shops • plating, stripping, and coating shops |
|
• sheet metal shops • machine shops and boiler shops |
4. Motor Vehicles and Transportation Equipment. Manufacturers of equipment and components of equipment for transporting passengers and cargo by land, air and water, including motor vehicles, aircraft, spacecraft, ships, boats, railroad and other vehicles such as motorcycles, bicycles and snowmobiles. Includes manufacture of motor vehicle parts and accessories; trailers and campers for attachment to other vehicles; self-contained motor homes; and van conversions. Does not include mobile home and modular home assembly (listed under "Lumber and Wood Products").
5. Stone and Cut Stone Product Manufacturing. An establishment that cuts, shapes, and/or finishes marble, granite, slate, and/or other stone for construction and miscellaneous uses. Does not include establishments engaged primarily in buying or selling partly finished monuments and tombstones ("Handcraft industries, Small-scale Manufacturing").
6. Structural Clay and Pottery Product Manufacturing. An establishment that produces brick and structural clay products, including pipe, china plumbing fixtures, vitreous china articles, and/or fine earthenware and porcelain products. Does not include artist/craftsman uses (see "Handcraft Industries and Small Scale Manufacturing," "Home Occupations").
7. Biodiesel Production. Fuel production from a mix of oil from biological sources (often waste oil), methanol and sodium hydroxide (lye). This can include mixing with petroleum diesel.
Manufacturing/Processing - Low Impact. A facility accommodating manufacturing processes involving and/or producing: apparel; food and beverage products; electronic, optical, and instrumentation products; ice; jewelry; and musical instruments. Low impact manufacturing also includes other establishments engaged in the assembly, fabrication, and conversion of already processed raw materials into products, where the operational characteristics of the manufacturing processes and the materials used are unlikely to cause significant impacts on surrounding land uses or the community. Examples of low impact manufacturing/processing uses include the following.
1. Artisan/Craft Product Manufacturing. Establishments manufacturing and/or assembling small products primarily by hand, including yarn, jewelry, pottery and other ceramics, as well as small glass and metal art and craft products.
2. Clothing and Fabric Product Manufacturing. An establishment that assembles clothing, draperies, and/or other products by cutting and sewing purchased textile fabrics, and related materials including leather, rubberized fabrics, plastics and furs. Does not include custom tailors and dressmakers not operating as a factory and not located on the site of a clothing store (see "Personal Services"). See also, "Manufacturing/Processing - High Impact - Textile and Leather Product Manufacturing."
3. Electronics, Equipment, and Appliance Manufacturing. An establishment that manufactures equipment, apparatus, and/or supplies for the generation, storage, transmission, transformation and use of electrical energy, including:
|
• appliances including stoves/ovens, refrigerators, freezers, laundry equipment, fans, vacuum cleaners, sewing machines • aviation instruments • computers, computer components, peripherals • electrical transmission and distribution equipment • electronic components and accessories, • semiconductors, integrated circuits, related devices • electrical welding apparatus • lighting and wiring equipment such as lamps and fixtures, wiring devices, vehicle lighting • industrial controls • instruments for measurement, testing, analysis and control, associated sensors and accessories • miscellaneous electrical machinery, equipment and supplies such as batteries, X-ray apparatus and tubes, electromedical and electrotherapeutic apparatus, electrical equipment for internal combustion engines |
|
• motors and generators • optical instruments and lenses • photographic equipment and supplies • radio and television receiving equipment • surgical, medical and dental instruments, equipment, and supplies • storage media, blank and pre-recorded, including magnetic, magneto-optical, and optical products such as compact disks (CDs), computer diskettes and hard drives, digital versatile disks (DVDs), magnetic tape products, phonograph records, etc. • surveying and drafting instruments • telephone and telegraph apparatus • transformers, switch gear and switchboards • watches and clocks |
Does not include testing laboratories (soils, materials testing, etc.) (see "Business Support Services"), or research and development facilities separate from manufacturing (see "Research and Development").
4. Food and Beverage Product Manufacturing. Manufacturing establishments producing or processing foods and beverages for human consumption, and certain related products. Examples of these uses include:
|
• bottling plants • breweries • candy, sugar and confectionery products manufacturing • catering services separate from stores or restaurants • coffee roasting • dairy products manufacturing • fats and oil product manufacturing |
|
• fruit and vegetable canning, preserving, related processing • grain mill products and by-products • meat, poultry, and seafood canning, curing • byproduct processing • soft drink production • miscellaneous food item preparation from raw products |
Does not include: retail bakeries; or beer brewing as part of a brew pub, bar or restaurant (see "Bar/Tavern," and "Night Club").
5. Handcraft Industries, Small-Scale Manufacturing. Establishments manufacturing and/or assembling small products primarily by hand, including yarn, jewelry, pottery and other ceramics, as well as small glass and metal art and craft products, and taxidermists. Also includes manufacturing establishments producing small products not classified in another major manufacturing group, including: brooms and brushes; buttons, costume novelties; musical instruments; pens, pencils, and other office and artists’ materials; sporting and athletic goods; toys; etc.
6. Paper Product Manufacturing. An establishment that converts pre-manufactured paper or paperboard into boxes, envelopes, paper bags, wallpaper, etc., and/or that coats or glazes pre-manufactured paper. Does not include the manufacturing of pulp, paper, or paperboard (see "Manufacturing - High Impact - Pulp and Pulp Product Manufacturing").
7. Photo/Film Processing Lab. A facility that provides high volume and/or custom processing services for photographic negative film, transparencies, and/or prints, where the processed products are delivered to off-site retail outlets for customer pick-up. Does not include small-scale photo processing machines accessory to other retail businesses.
8. Winery. A manufacturing facility where wine grapes are crushed, fermented, aged, bottled, and sold at wholesale as finished wine. May include tasting and accessory retail sales of wine produced on site.
Map Act. See "Subdivision Map Act."
Market Rate. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Maximum Allowable Residential Density. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
May. That which is permissible.
Median Strip. The dividing area, either paved or landscaped, between opposing lanes of traffic on a roadway.
Media Production. Facilities for motion picture, television, video, sound, computer, and other communications media production. These facilities include the following types.
1. Backlots/outdoor facilities. Outdoor sets, backlots, and other outdoor facilities, including supporting indoor workshops and craft shops.
2. Indoor support facilities. Administrative and technical production support facilities, including administrative and production offices, post-production facilities (editing and sound recording studios, foley stages, etc.), optical and special effects units, film processing laboratories, etc.
3. Soundstages. Warehouse-type facilities providing space for the construction and use of indoor sets, including supporting workshops and craft shops.
Revised by Ord. #1382 - Effective 12/22/08
Medicinal Cannabis. Means cannabis used in strict accordance with the Compassionate Use Act of 1996 (Health and Safety Code Section 11362.5 et seq.) and Senate Bill 94, also known as the Medicinal and Adult-Use Cannabis Regulation and Safety Act (Division 10 of the Business and Professions Code, Section 26000 et seq.).
2. Medicinal Cannabis Identification Card. A document issued by the State Department of Health Services that identifies a person authorized to engage in the medicinal use of cannabis and the person’s designated primary caregiver, if any, as per California Health and Safety Code Section 11362.7, and as may be amended.
3. Person with an Identification Card. Means an individual who is a qualified patient who has applied for and received a valid identification card pursuant to this article as per the California Health and Safety Code Section 11362.7, and as may be amended.
4. Primary Caregiver. Means the individual, designated by a qualified patient or by a person with an identification card, who has consistently assumed responsibility for the housing, health, or safety of that patient or person, as more particularly as set forth in California Health and Safety Code Section 11362.7, and as may be amended.
5. Qualified Patient. Means a person who is entitled to the protections of Section 11362.5 of the California Health and Safety Code, but who does not have an identification card issued pursuant to this article as set forth in California Health and Safety Code Section 11362.7, and as may be amended.
Medical Services - Clinic, Urgent Care. A facility other than a hospital where medical, mental health, surgical and other personal health services are provided on an outpatient basis. Examples of these uses include:
|
• medical offices with four or more licensed practitioners and/or medical specialties |
|
• out-patient care facilities • urgent care facilities • other allied health services |
These facilities may also include accessory medical laboratories. Counseling services by other than medical doctors or psychiatrists are included under "Offices - Professional."
Revised by Ord. #1382 - Effective 12/22/08
Medical Services - Doctor Office. A facility other than a hospital where medical, dental, mental health, surgical, and/or other personal health care services are provided on an outpatient basis, and that accommodates no more than three licensed primary practitioners (for example, chiropractors, medical doctors, psychiatrists, etc.) within an individual office suite. Counseling services by other than medical doctors or psychiatrists are included under "Offices - Professional."
Medical Services - Extended Care. Residential facilities providing nursing and health-related care as a primary use with in-patient beds. Examples of these uses include: board and care homes; convalescent and rest homes; extended care facilities; and skilled nursing facilities. Long-term personal care facilities that do not emphasize medical treatment are included under "Residential Care."
Medical Services - Hospital. Hospitals and similar facilities engaged primarily in providing diagnostic services, and extensive medical treatment, including surgical and other hospital services. These establishments have an organized medical staff, inpatient beds, and equipment and facilities to provide complete health care. May include on-site accessory clinics and laboratories, accessory retail uses and emergency heliports (see the separate definition of "Accessory Retail Uses").
Meeting Facility, Public or Private. A facility for public or private meetings, including community centers, religious facilities (e.g., churches, mosques, synagogues, etc.), civic and private auditoriums, grange halls, union halls, meeting halls for clubs and other membership organizations, etc. Also includes functionally related internal facilities such as kitchens, multi-purpose rooms, and storage. Does not include conference and meeting rooms accessory and incidental to another primary use that are typically used only by on-site employees and clients, and occupy less floor area on the site than the offices they support (see "Offices"). Does not include: theaters, sports or other commercial entertainment facilities (see "Theater," and "Sports and Entertainment Assembly"); or convention centers (see "Conference/Convention Facility"). Related on-site facilities including day care centers and schools are separately defined.
Mercalli Intensity Scale. A subjective measure of the observed effects (human reactions, structural damage, geologic effects) of an earthquake. Expressed in Roman numerals from I to XII.
Microclimate. See "Landscaping Standards."
Mineral Resource. Land on which known deposits of commercially viable mineral or aggregate deposits exist. This designation is applied to sites determined by the State Division of Mines and Geology as being a resource of regional significance, and is intended to help maintain the quarrying operations and protect them from encroachment of incompatible land uses.
Ministerial (Administrative) Decision. An action taken by a governmental agency that follows established procedures and rules and does not call for the exercise of judgment in deciding whether to approve a project.
Mitigate. To ameliorate, alleviate, or avoid to the extent reasonably feasible.
Mixed-Use. Properties on which various uses, such as office, commercial, institutional, and residential, are combined in a single building or on a single site in an integrated development project with significant functional interrelationships and a coherent physical design. A "single site" may include contiguous properties.
Mobile Home. A trailer, transportable in one or more sections, that is certified under the National Manufactured Housing Construction and Safety Standards Act of 1974, which is over eight feet in width and 40 feet in length, is tied down (a) to a permanent foundation on a lot either owned or leased by the homeowner or (b) is set on piers, with wheels removed and skirted, in a mobile home park and not including recreational vehicle, commercial coach or factory-built housing. A mobile home on a permanent foundation is included under the definition of "Single-Family Dwellings." (See also "Manufactured Housing" and "Modular Unit.")
Mobile Home Park. Any site that is planned and improved to accommodate two or more mobile homes used for residential purposes, or on which two or more mobile home lots are rented, leased, or held out for rent or lease, or were formerly held out for rent or lease and later converted to a subdivision, cooperative, condominium, or other form of resident ownership, to accommodate mobile homes used for residential purposes. May include a common storage area for recreational vehicles owned by residents only.
Mobile Home, RV, and Boat Sales. Retail establishments selling both mobile home dwelling units, and/or various vehicles and watercraft for recreational uses. Includes the sales of boats, campers and camper shells, jet skis, mobile homes, motor homes, and travel trailers.
Mobile Recycling Unit. See "Recycling Facility."
Moderate Income Household. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Modular Unit. A factory-fabricated, transportable building or major component designed for use by itself or for incorporation with similar units on-site into a structure for residential, commercial, educational, or industrial use. Differs from mobile homes and manufactured housing by (in addition to lacking an integral chassis or permanent hitch to allow future movement) being subject to California housing law design standards. California standards are more restrictive than federal standards in some respects (e.g., plumbing and energy conservation). Also called Factory-built Housing and regulated by State law of that title. (See "Mobile Home" and "Manufactured Housing.")
Mortuary, Funeral Home. Funeral homes and parlors, where deceased are prepared for burial or cremation, and funeral services may be conducted.
Multi-Family Housing. A dwelling unit that is part of a structure containing two or more dwelling units excluding second units. Multi-family dwellings include: duplexes, triplexes, fourplexes (buildings under one ownership with two, three or four dwelling units, respectively, in the same structure); apartments (five or more units under one ownership in a single building); transitional housing; and permanent supportive housing and single room occupancy housing where people live as independently as possible with the assistance of social services tailored to each person’s needs.
Multiplier Effect. The recirculation of money through the economy multiplies its impact on jobs and income. For example, money paid as salaries to industrial and office workers is spent on housing, food, clothes and other locally-available goods and services. This spending creates jobs in housing construction, retail stores (e.g., grocery and drug stores) and professional offices. The wage paid to workers in those industries is again re-spent, creating still more jobs. Overall, one job in basic industry is estimated to create approximately one more job in non-basic industry.
Municipal Services. Services traditionally provided by local government, including water and sewer, roads, parks, schools, and police and fire protection.
Mural. A very large image, such as a painting or enlarged photograph, applied directly to a wall or ceiling.
Must. That which is mandatory.
N Definitions, "N."
National Ambient Air Quality Standards. The prescribed level of pollutants in the outside air that cannot be exceeded legally during a specified time in a specified geographical area.
National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). An act passed in 1974 establishing federal legislation for national environmental policy, a council on environmental quality, and the requirements for environmental impact statements.
National Historic Preservation Act of 1966 (NHPA). See "Historical Resource Preservation."
National Register of Historic Places. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Native Species. See "Landscaping Standards."
Natural or Existing Grade. See "Grading."
Natural Area. See "Trees."
Natural State. The condition existing prior to development or alteration of a site.
Nature Preserves, Habitat and Wetland Restoration. Natural resource and habitat areas that are managed and protected to preserve and/or restore and rehabilitate the value of the subject resources.
Negative Declaration. A statement describing the reasoning that a proposed action will not have a significant adverse effect on the environment, in compliance with the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA).
Neighborhood. A planning area commonly identified as such in a community’s planning documents, and by the individuals residing and working within the neighborhood. Documentation may include a map prepared for planning purposes, on which the names and boundaries of the neighborhood are shown.
Neighborhood Conservation Area (NCA). See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Neighborhood Park. City- or county-owned land intended to serve the recreation needs of people living or working within one-half mile radius of the park.
Night Club. A facility serving alcoholic beverages for on-site consumption, and providing entertainment, examples of which include live music and/or dancing, comedy, etc.
Noise. Any sound that is undesirable because it interferes with speech and hearing, or is intense enough to damage hearing, or is otherwise annoying. Noise, simply, is "unwanted sound."
1. Community Noise Equivalent Level (CNEL). A 24-hour energy equivalent level derived from a variety of single-noise events, with weighting factors of 5 and 10 dBA applied to the evening (7 PM to 10 PM) and nighttime (10 p.m. to 7 A.m.) periods, respectively, to allow for the greater sensitivity to noise during these hours.
2. dB, Decibel. A unit used to express the relative intensity of a sound as it is heard by the human ear.
3. dBA. The "A-weighted" scale for measuring sound in decibels; weighs or reduces the effects of low and high frequencies in order to simulate human hearing. Every increase of 10 dBA doubles the perceived loudness though the noise is actually ten times more intense.
4. Ldn. Day-Night Average Sound Level. The A-weighted average sound level for a given area (measured in decibels) during a 24-hour period with a 10 dB weighting applied to night-time sound levels. The Ldn is approximately numerically equal to the CNEL for most environmental settings.
5. Leq. The energy equivalent level, defined as the average sound level on the basis of sound energy (or sound pressure squared). The Leq is a "dosage" type measure and is the basis for the descriptors used in current standards, such as the 24-hour CNEL used by the State of California.
6. L10. A statistical descriptor indicating peak noise levels, i.e. the sound level exceeded 10 percent of the time. It is a commonly used descriptor of community noise, and has been used in Federal Highway Administration standards and the standards of some cities and counties.
7. Noise Attenuation. Reduction of the level of a noise source using a substance, material, or surface, such as earth berms and/or solid concrete walls.
8. Noise Contour. A line connecting points of equal noise level as measured on the same scale. Noise levels greater than the 60 Ldn contour (measured in dBA) require noise attenuation in residential development.
Non-Attainment. The condition of not achieving a desired or required level of performance. Frequently used in reference to air quality. (See "Attainment.")
Nonconforming Parcel. A parcel that was legally created prior to the adoption of this Land Use Code or amendment, but does not comply with the current area, width, depth, or other applicable requirements of this Land Use Code.
Nonconforming Sign. See "Signs."
Nonconforming Structure. A structure that was legally constructed prior to the adoption or amendment of this Land Use Code, but does not comply with the current setback, height limit, and/or other applicable requirements of this Land Use Code.
Nonconforming Use. A use of land and/or a structure (either conforming or nonconforming) that was legally established and maintained prior to the adoption of this Land Use Code or amendment, but does not conform to the current Land Use Code requirements for allowable land uses within the applicable zoning district.
Non-Contributing Structure or Building. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Non-Prime Agricultural Land. Non-prime agricultural land consists of property used for the production of food or fiber, with soils that qualify for rating as classes III through VII in the Soil Conservation Service land capability classifications.
Noteworthy Structures. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
O Definitions, "O."
Occupancy. All or a portion of a structure occupied by one tenant.
Off-Sale Liquor Establishment. Any establishment at which alcohol is sold, served, or given to patrons, to be consumed off-site, except food markets, supermarkets, drugstores, and other retail establishments in which the sale of alcohol for off-site use constitutes less than 20 percent of the total sales.
Off-Site. An activity or accessory use that is related to a specific primary use, but is not located on the same site as the primary use. For an affordable housing project, it is the area outside of the boundaries of the residential project.
Office. This Land Use Code distinguishes between the following types of offices. These do not include medical offices (see "Medical Service - Clinic, Laboratory, Urgent Care," and "Medical Service - Doctor Office").
1. Accessory. Office facilities that are incidental and accessory to another business or sales activity that is the primary use.
2. Business/Service. Establishments providing direct services to consumers. Examples of these uses include employment agencies, insurance agent offices, real estate offices, travel agencies, utility company offices, etc. This use does not include "Bank, Financial Services," which are separately defined.
3. Government. Administrative, clerical, or public contact and/or service offices of a local, state, or federal government agency or service facilities. Includes post offices, but not bulk mailing distribution centers, which are under "Truck or Freight Terminal."
4. Processing. Office-type facilities characterized by high employee densities, and occupied by businesses engaged in information processing, and other computer-dependent and/or telecommunications-based activities. Examples of these uses include:
|
• airline, lodging chain, and rental car company reservation centers • computer software and hardware design and development • consumer credit reporting • data processing services • health management organization (HMO) offices where no medical services are provided |
|
• insurance claim processing • mail order and electronic commerce transaction processing • telecommunications facility design and management • telemarketing |
5. Professional. Office-type facilities occupied by businesses that provide professional services and/or engaged in the production of intellectual property. Examples of these uses include:
|
• accounting, auditing and bookkeeping services • advertising agencies • attorneys • commercial art and design services • construction contractors (office facilities only) • counseling services • court reporting services • detective agencies and similar services • design services including architecture, engineering, landscape architecture, urban planning • educational, scientific and research organization |
|
• financial management and investment counseling • literary and talent agencies • management and public relations services • media postproduction services • news services • photographers and photography studios • psychologists • secretarial, stenographic, word processing, and temporary clerical employee services • security and commodity brokers • writers and artists offices |
6. Temporary. A mobile home, recreational vehicle or modular unit used as a temporary office facility. Temporary Offices may include: construction supervision offices on a construction site or off-site construction yard; a temporary on-site real estate office for a development project; or a temporary business office in advance of permanent facility construction.
7. Temporary Real Estate. The temporary use of a dwelling unit within a residential development project as a sales office for the units on the same site, which is converted to residential use at the conclusion of its office use.
Office of Historic Preservation (OHP). See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Office-Supporting Retail. A retail store that carries one or more types of merchandise that will typically be of frequent interest to and/or needed by the various businesses listed under the definition of "Office," and/or the employees of those businesses. Examples of these types of merchandise include:
|
• Books • Computer equipment • Flowers |
|
• Newspapers and magazines • Office supplies, stationery • Photographic supplies and cameras |
On-Sale Liquor Establishment. Any establishment at which alcohol is sold, served, or given to patrons, to be consumed on-site.
On-Site. An activity or accessory use that is related to a specific primary use, which is located on the same site as the primary use.
Open Fencing. A barrier constructed of material which is transparent, such as glass, plastic panels or wrought iron.
Open Space Land. Any parcel or area of land or water that is essentially unimproved and devoted to an open space use for the purposes of (1) the preservation of natural resources, (2) the managed production of resources, (3) outdoor recreation, or (4) public health and safety.
Ordinance. A law or regulation set forth and adopted by a governmental authority, usually a city or county.
Ordinary Maintenance and Repair. Work for which a Building Permit is not required, the purpose and effect of which is to correct deterioration of or damage to a structure or any part thereof and to restore the structure to its condition before the deterioration or damage.
Organization, Organizational Entity. Any public or private corporation, political subdivision, partnership, firm, trust or estate or any other legal entity whatsoever, which is recognized by law.
Organizational House. A residential lodging facility operated by a membership organization for its members and not open to the general public. Includes fraternity and sorority houses, student dormitories, convents, monasteries, and religious residential retreats.
Outdoor Recreation Use. A privately or publicly owned or operated use providing facilities for outdoor recreation activities.
Outdoor Retail Sales and Activities. Permanent and mobile outdoor sales and rental establishments including auction yards, flea markets, lumber and other material sales yards, newsstands, outdoor facilities for the sale or rental of vehicles/equipment, and other uses where the business is not conducted entirely within a structure. Outdoor retail sales and activities shall comply with the standards for "Outdoor Displays and Sales" in Section 9.42.140.
Overlay. A land use designation on the General Plan Land Use Map, or a zoning designation on a zoning map, that modifies the basic underlying designation in some specific manner.
Overspray. See "Landscaping Standards."
Owner. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
P Definitions, "P."
Parking Area, Public. An open area, excluding a street or other public way, used for the parking of automobiles and available to the public, whether for free or for compensation.
Parking Facility. Parking space or shelter for automobiles or other vehicles.
1. A garage is an attached or detached accessory structure, which is enclosed on at least three sides;
2. A carport is an attached or detached accessory structure, which is not enclosed on more than two sides;
3. A car deck is an unenclosed platform providing off-street parking spaces, normally constructed at the street level of a sloping lot.
Parking, Shared. A public or private parking area used jointly by two or more uses.
Park Land, Parkland. Land that is publicly owned or controlled for the purpose of providing parks, recreation, or open space for public use.
Parks and Playgrounds. A public outdoor recreation facility that may provide a variety of recreational opportunities including playground equipment, open space areas for passive recreation and picnicking, and sport and active recreation facilities.
Parkway Strip. A piece of land located between the rear of a curb and the front of a sidewalk, usually used for planting low ground cover and/or street trees, also known as "planter strip."
Pedestrian Orientation. Any physical structure or place with design qualities and elements that contribute to an active, inviting and pleasant place for pedestrians including:
1. Building facades that are highly articulated at the street level, with interesting uses of material, color, and architectural detailing, located directly behind the sidewalk;
2. Design amenities related to the street level such as awnings, paseos, arcades;
3. Visibility into buildings at the street level;
4. A continuous sidewalk, with a minimum of intrusions into pedestrian right-of-way;
5. Continuity of building facades along the street with few interruptions in the progression of buildings and stores;
6. Signs oriented and scaled to the pedestrian rather than the motorist;
7. Landscaping; and
8. Street furniture.
Pedestrian Oriented Use. A land use that is intended to encourage walk-in customers and that generally does not limit the number of customers by requiring appointments or otherwise excluding the general public. A pedestrian oriented use provides spontaneous draw from sidewalk and street due to visual interest, high customer turnover, and social interaction.
Performance Standards. Zoning regulations that permit uses based on a particular set of standards of operation rather than on particular type of use. Performance standards provide specific criteria limiting noise, air pollution, emissions, odors, vibration, dust, dirt, glare, heat, fire hazards, wastes, traffic impacts, and visual impact of a use.
Person. Any natural person, individual, corporation, or organizational entity, as further identified in the Arcata Municipal Code (AMC § 1100) and in the California Civil Code (Civil Code § 14), which is recognized in law as the subject of rights or duties.
Person with an Identification Card. See "Medicinal Cannabis."
Personal Services. Establishments providing non-medical services to individuals as a primary use. Examples of these uses include:
|
• barber and beauty shops • clothing rental • dry cleaning pick-up stores with limited equipment • home electronics and small appliance repair • laundromats (self-service laundries) |
|
• locksmiths • massage (licensed, therapeutic, non-sexual) • pet grooming with no boarding • shoe repair shops • tailors • tanning salons |
These uses may also include accessory retail sales of products related to the services provided.
Personal Services - Restricted. Personal services that may tend to have a blighting and/or deteriorating effect upon surrounding areas and which may need to be dispersed to minimize their adverse impacts. Examples of these uses include:
|
• check cashing stores • fortune tellers • palm and card readers • pawnshops |
|
• psychics • spas and hot tubs for hourly rental • tattoo and body piercing services |
Pet Shop. A store that sells household pets and pet supplies.
Pipeline, Utility Transmission or Distribution Line. Transportation facilities for the conveyance of water or commodities other than petroleum. Also includes pipeline surface and terminal facilities, including pump stations, bulk stations surge and storage tanks. Utility lines include facilities for the transmission of electrical energy for sale, including transmission lines for a public utility company. Also includes telephone, telegraph, cable television and other communications transmission facilities utilizing direct physical conduits. Does not include offices or service centers (see Office), or distribution substations.
Planned Development (PD). Development of land as a single unit by taking advantage of modern site planning techniques to result in a more efficient use of land and a better living environment than is otherwise possible through strict application of development standards. Planned developments allow for exceptions and deviations from standard zoning requirements in exchange for creative design and added amenities.
Planning Area. The area directly addressed by the general plan. A city’s planning area typically encompasses the city limits, potentially annexable land within its sphere of influence, and surrounding lands which affect the City.
Planning Commission. The City of Arcata Planning Commission, appointed by the Arcata City Council in compliance with Government Code Section 65101. A body, usually having five or seven members, created by a city or county in compliance with California law which requires the assignment of the planning functions of the city or county to a planning department, planning commission, hearing officers, and/or the legislative body itself, as deemed appropriate by the legislative body.
Planning Permit. Authority granted by the City to use a specified site for a particular purpose. "Planning Permit" includes Use Permits, Minor Use Permits, Coastal Permits, Variances, Planned Development Permits, Emergency Permits, Design Review, Certificates of Occupancy and Zoning Clearances, as established by Article 7 (Planning Permit Procedures).
Plant Nursery. A commercial agricultural establishment engaged in the production of ornamental plants and other nursery products, grown under cover either in containers or in the soil on the site, or outdoors in containers. The outdoor production of ornamental plants in the soil on the site is instead included under "Crop Production, Horticulture, Orchard, Vineyard." Also includes establishments engaged in the sale of these products (e.g., wholesale and retail nurseries) and commercial-scale greenhouses (home greenhouses are included under "Residential Accessory Use or Structure"). The sale of house plants or other nursery products entirely within a building is also included under "General Retail."
Policy. A group of related actions or means that will be employed to achieve objectives.
Pollution, Non-Point. Sources for pollution that are less definable and usually cover broad areas of land, such as agricultural land with fertilizers that are carried from the land by runoff, or automobiles.
Pollution, Point. In reference to air or water quality, a discrete source from which pollution is generated before it enters receiving waters or air, such as a sewer outfall, a smokestack, or an industrial waste pipe.
Porous Mulch. See "Landscaping Standards."
Poverty Level. As used by the U.S. Census, families and unrelated individuals are classified as being above or below the poverty level based on a poverty index that provides a range of income cutoffs or "poverty thresholds" varying by size of family, number of children, and age of householder. The income cutoffs are updated each year to reflect the change in the Consumer Price Index.
Preservation. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Preserve, n. An area in which beneficial uses in their present condition are protected; for example, a nature preserve or an agricultural preserve. (See "Agricultural Preserve")
Primary Caregiver. See "Medicinal Cannabis."
Primary Structure. A structure that accommodates the primary use of the site.
Primary Use. The main purpose for which a site is developed and occupied, including the activities that are conducted on the site a majority of the hours during which activities occur.
Primary Zoning District. The zoning district applied to a site by the Zoning Map, to which an overlay zoning district may also be applied.
Prime Agricultural Land. Means any of the following, in compliance with Williamson Act Section 51201:
1. All land that qualifies for rating as Class I or Class II in the Soil Conservation Service land capability classifications.
2. Land that qualifies for a rating of 60 through 100 in the Storie Index Rating.
3. Land that supports livestock used for the production of food and fiber and which has an annual carrying capacity equivalent to at least one animal unit per acre as defined by the United States Department of Agriculture.
4. Land planted with fruit- or nut-bearing trees, vines, bushes, or crops that have a nonbearing period of less than five years and which will normally return during the commercial bearing period on an annual basis from the production of unprocessed agricultural plant production not less than $200 per acre.
5. Land that has returned from the production of unprocessed agricultural plant products an annual gross value of not less than $200 per acre for three of the previous five years.
Prime Farmland. Land which has the best combination of physical and chemical characteristics for the production of crops. Prime Farmland must have been used for the production of irrigated crops within the last three years. Prime Farmland does not include publicly-owned lands for which there is an adopted policy preventing agricultural use. (See "Prime Agricultural Land.")
Printing and Publishing. An establishment engaged in printing by letterpress, lithography, gravure, screen, offset, or electrostatic (xerographic) copying; and other establishments serving the printing trade such as bookbinding, typesetting, engraving, photoengraving and electrotyping. This use also includes establishments that publish newspapers, books and periodicals; establishments manufacturing business forms and binding devices. "Quick printing" services are included in the definition of "Business Support Services."
Private Residential Recreation Facility. A privately-owned, non-commercial recreation facility provided for residential project or neighborhood residents, including swimming pools, swim and tennis clubs, park and sport court facilities. Does not include golf courses and country clubs, which are separately defined.
Private Road/Private Street. Privately owned (and usually privately maintained) motor vehicle access that is not dedicated as a public street. Typically the owner posts a sign indicating that the street is private property and limits traffic in some fashion. For density calculation purposes, some jurisdictions exclude private roads when establishing the total acreage of the site; however, aisles within and driveways serving private parking lots are not considered private roads.
Processing Facility. See "Recycling Facility."
Produce Stand. A temporary business established and operated for a specific time, selling fruits, vegetables, nuts, firewood and other agricultural produce.
Production of Food or Fiber. Any type of commercial agricultural operation that produces food or fiber products, including but not limited to all types of: irrigated field crop production (vegetables, fruits, grains, seed crops, etc.), dry farming operations (grain, etc.), orchards and vineyards, berries, etc.; and animal raising operations such as the raising of cattle, fowl or poultry, goats, sheep, swine, or other animals used for food or clothing products; but not including timber production.
Property Line. The recorded boundary of a parcel of land.
Proposed Project. A proposed new structure, new addition to an existing structure, or area of other new site development; these do not include the alteration of any portion of an existing structure other than an addition.
Public Buildings and Uses. Facilities owned and operated by the City, and/or State or Federal governments, or a local agency (e.g., a special district).
Public and Quasi-public Facilities. Institutional, academic, governmental and community service uses, either owned publicly or operated by non-profit organizations, including private hospitals and cemeteries.
Public Nuisance. Anything which is injurious to human health or is indecent or offensive to the senses and interferes with the comfortable enjoyment of life or property, and affects at the same time an entire community, neighborhood, household or any considerable number of persons although the extent of annoyance or damage inflicted upon an individual may be unequal.
Public Safety Facility. A facility operated by a public agency including fire stations, other fire prevention and fire fighting facilities, police and sheriff substations and headquarters, including interim incarceration facilities.
Public Services. See "Municipal Services."
Public Trust Lands. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Q Definitions, "Q."
Qualified Patient. See "Medicinal Cannabis."
Qualifying Resident. A senior citizen or other person eligible to reside in senior citizen housing.
R Definitions, "R."
Reclamation. The reuse of resources, usually those present in solid wastes or sewage.
Reconstruction. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Recordation, County. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Recreational Vehicle (RV). A motor home, travel trailer, truck camper, or camping trailer, with or without motive power, originally designed for human habitation for recreational, emergency, or other occupancy, which:
1. Contains less than 320 square feet of internal living room area, excluding built-in equipment, including wardrobe, closets, cabinets, kitchen units or fixtures, and bath or toilet rooms; and
2. Contains 400 square feet or less of gross area measured at maximum horizontal projections; and
3. Is built on a single chassis; and
4. Is either self-propelled, truck-mounted, or permanently towable on the highways without a towing permit.
Recreational Vehicle (RV) Park. See "Lodging."
Recreational Use. The use of land by the public, with or without charge, for walking, hiking, picnicking, camping, swimming, boating, fishing, hunting, or other outdoor games or sports for which facilities are provided for public participation.
Recycling Facility. This land use type includes a variety of facilities involved with the collection, sorting and processing of recyclable materials.
1. Collection Facility. A center where the public may donate, redeem or sell recyclable materials, which may include the following, where allowed by the applicable zoning district:
b. Small collection facilities which occupy an area of 350 square feet or less and may include:
(1) A mobile unit;
(2) Bulk reverse vending machines or a grouping of reverse vending machines occupying more than 50 square feet; and
(3) Kiosk-type units which may include permanent structures.
c. Large collection facilities which occupy an area of more than 350 square feet and/or include permanent structures.
2. Mobile Recycling Unit. An automobile, truck, trailer, or van used for the collection of recyclable materials, carrying bins, boxes, or other containers.
3. Processing Facility. A structure or enclosed space used for the collection and processing of recyclable materials for shipment, or to an end-user’s specifications, by such means as baling, briquetting, cleaning, compacting, crushing, flattening, grinding, mechanical sorting, re-manufacturing and shredding. Processing facilities include the following types, both of which are included under the definition of "Scrap and Dismantling Yards," below:
a. Light processing facility occupies an area of under 45,000 square feet of collection, processing and storage area, and averages two outbound truck shipments each day. Light processing facilities are limited to baling, briquetting, compacting, crushing, grinding, shredding and sorting of source separated recyclable materials sufficient to qualify as a certified processing facility. A light processing facility shall not shred, compact, or bale ferrous metals other than food and beverage containers; and
b. A heavy processing facility is any processing facility other than a light processing facility.
4. Recycling Facility. A center for the collection and/or processing of recyclable materials. A "certified" recycling or processing facility is certified by the California Department of Conservation as meeting the requirements of the California Beverage Container Recycling and Litter Reduction Act of 986. A recycling facility does not include storage containers located on a residentially, commercially or industrially designated site used solely for the recycling of material generated on the site. See "Collection Facility" above.
5. Recycling or Recyclable Material. Reusable domestic containers and other materials which can be reconstituted, re-manufactured, or reused in an altered form, including glass, metals, paper and plastic. Recyclable material does not include refuse or hazardous materials.
6. Reverse Vending Machine. An automated mechanical device which accepts at least one or more types of empty beverage containers and issues a cash refund or a redeemable credit slip with a value not less than the container’s redemption value, as determined by State law. These vending machines may accept aluminum cans, glass and plastic bottles, and other containers.
A bulk reverse vending machine is a reverse vending machine that is larger than 50 square feet, is designed to accept more than one container at a time, and issues a cash refund based on total weight instead of by container.
7. Scrap and Dismantling Yards. Outdoor establishments primarily engaged in assembling, breaking up, sorting, and the temporary storage and distribution of recyclable or reusable scrap and waste materials, including auto wreckers engaged in dismantling automobiles for scrap, and the incidental wholesale or retail sales of parts from those vehicles. Includes light and heavy processing facilities for recycling (see the definitions above). Does not include: places where these activities are conducted entirely within buildings; pawn shops, and other secondhand stores; the sale of operative used cars; or landfills or other waste disposal sites.
Regional. Pertaining to activities or economies at a scale greater than that of a single jurisdiction, and affecting a broad geographic area.
Regional Information Center. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Rehabilitation. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Religious Facility. A permanent facility operated by a religious organization exclusively for worship, or the promotion of religious activities, including accessory uses on the same site. Examples of these types of facilities include churches, mosques, synagogues, and temples. Examples of allowable accessory uses on the same site include living quarters for ministers and staff, facilities for child day care and religious instruction operated at the same time as religious services (where authorized by the same type of land use permit required for the religious facility itself). May also include fund-raising sales, bazaars, dinners, parties, or other indoor and outdoor events on the same site. Other facilities maintained by religious organizations, including full-time day care centers, full-time educational institutions, hospitals and other potentially related operations (for example, a recreational camp) are defined in this Chapter according to their respective activities. Does not include the temporary use of an approved public assembly facility (for example, a private meeting hall, community center, theater, or auditorium) by a congregation for religious meetings, which is instead defined under the type of meeting facility hosting the congregation.
Remodeling. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Repair Service - Equipment, Large Appliances, etc. A service and facility where various types of electrical, electronic, and mechanical equipment, and home and business appliances are repaired and/or maintained away from the site of the equipment owner. Does not include vehicle repair or maintenance, which is included under "Vehicle Services", the repair of small home appliances and electronic equipment, which is included under "Personal Services", or maintenance and repair activities that occur on the client’s site, which are included under "Maintenance Service - Client Site Services."
Replacement Cost. The construction cost to replace an entire structure.
Research and Development Use. A use engaged in study, testing, design, analysis, and experimental development of products, processes, or services.
Residential. Land designated in the City or County General Plan and zoning ordinance for buildings consisting of dwelling units. May be improved, vacant, or unimproved. (See "Dwelling Unit.")
Residential Accessory Use or Structure. Any use and/or structure that is customarily a part of, and clearly incidental and secondary to, a residence, and does not change the character of the residential use. This definition includes the following accessory structures, and other similar structures normally associated with a residential use of property. See also "Agricultural Accessory Structure."
|
• garages • gazebos • greenhouses (non-commercial) • guest houses • home satellite dishes and receiving antennas per Section 9.44.030.B • second units |
|
• spas and hot tubs • storage sheds • studios • swimming pools • tennis and other on-site sport courts • workshops |
Also includes the indoor storage of automobiles (including their incidental restoration and repair), personal recreational vehicles and other personal property, accessory to a residential use.
Residential Care Facility. A single dwelling unit or multiple-unit facility licensed or supervised by a Federal, State, or local health/welfare agency that provides 24-hour non-medical care of unrelated persons who are handicapped and in need of personal services, supervision, or assistance essential for sustaining the activities of daily living or for the protection of the individual in a family-like environment.
Residential Care Facility for the Elderly (RCFE). A housing arrangement chosen voluntarily by the residents, or the residents’ guardians, conservators or other responsible persons; where 75 percent of the residents are at least 62 years of age, or, if younger, have needs compatible with other residents; and where varying levels of care and supervision are provided, as agreed to at the time of admission or as determined necessary at subsequent times of reappraisal (definition from California Code of Regulations Title 22, Division 6, Chapter 6, Residential Care Facilities for the Elderly). RCFE projects may include basic services and community space. RCFE projects include assisted living facilities (board and care homes), congregate housing, independent living centers/senior apartments, and life care facilities as defined below.
1. Assisted Living Facility. A residential building or buildings that also provide housing, personal and health care, as permitted by the Department of Social Services, designed to respond to the daily, individual needs of the residents. Assisted Living Facilities may include kitchenettes (small refrigerator, sink and/or microwave oven) within individual rooms. Assisted Living Facilities are required to be licensed by the California Department of Social Services, and do not include skilled nursing services.
2. Independent Living Center/Senior Apartment. Independent living centers and senior apartments and are multi-family residential projects reserved for senior citizens, where common facilities may be provided (for example, recreation areas), but where each dwelling unit has individual living, sleeping, bathing, and kitchen facilities.
3. Life Care Facility. Sometimes called Continuing Care Retirement Communities, or Senior Continuum of Care Complex, these facilities provide a wide range of care and supervision, and also provide health care (skilled nursing) so that residents can receive medical care without leaving the facility. Residents can expect to remain, even if they become physically incapacitated later in life. Life Care Facilities require multiple licensing from the State Department of Social Services, the State Department of Health Services, and the State Department of Insurance.
Residential Floor Area. The sum of the floor area for each of a residential structure’s stories measured from the exterior limits of the faces of the structure. The residential floor area does not include: basements, attics, cellars, storage rooms accessible from the exterior of the structure, any floor space which is designated for the parking of motor vehicles, or covered or uncovered porches unless said area meets the Uniform Building Code (UBC) standards for habitable floor area. Note that certain spaces, such as bathrooms, closets, and storage rooms accessed from the interior of the structure which are not "habitable area" as defined by the UBC are considered "residential floor area" for the purpose of this Land Use Code.
Residential, Multiple Family. See "Multi-family housing."
Residential, Single-Family. See "Single family dwelling."
Residential Zoning District. Any of the residential zoning districts established by Section 9.12.020 (Zoning Map and Zoning Districts).
Resources, Non-Renewable. Refers to natural resources, such as fossil fuels and natural gas that, once used, cannot be replaced and used again.
Restaurant, Cafe, Coffee Shop. A retail business operating as a permanent food facility1, principally engaged in selling menu-ordered, ready-to-eat food1, which may include food that is edible with no, or minimal, additional preparation, and/or beverages prepared for on- or off-premises consumption, which is provided through counter service, table service, drive-through, delivery, or other means. (See also Bar, Pub, Tavern).
Restaurant, Fast-Food. Any retail establishment intended primarily to provide short-order food services for on-site dining and/or take-out, including self-serve restaurants (excluding cafeterias where food is consumed on the premises), drive-in restaurants, and formula restaurants. Also see "Restaurant, Formula."
Restaurant, Formula. A restaurant, cafe, coffee shop that is required by contractual or other arrangement to offer any of the following: standardized menus, ingredients, food preparation, decor, uniforms, architecture, signs or similar standardized features, which causes it to be substantially identical to more than 11 other restaurants, cafes, coffee shops, regardless of ownership or location.
Restore. To renew, rebuild, or reconstruct to a former state.
Restrict. To check, bound, or decrease the range, scope, or incidence of a particular condition.
Retention Basin/Retention Pond. See "Detention Basin/Detention Pond."
Retrofit. To add materials and/or devices to an existing building or system to improve its operation, safety, or efficiency. Buildings have been retrofitted to use solar energy and to strengthen their ability to withstand earthquakes, for example.
Reverse Vending Machine. See "Recycling Facility."
Review Authority. The individual or official City body (the Community Development Director, Zoning Administrator, Environmental Coordinator, Planning Commission, Historic and Design Review Authority, or City Council) identified by this Land Use Code as having the responsibility and authority to review, and approve or disapprove the permit applications described in Article 7 (Planning Permit Procedures).
Rezoning. An amendment to the map and/or text of a zoning ordinance to effect a change in the nature, density, or intensity of uses allowed in a zoning district and/or on a designated parcel or land area.
Richter Scale. A measure of the size or energy release of an earthquake at its source. The scale is logarithmic; the wave amplitude of each number on the scale is ten times greater than that of the previous whole number.
Rideshare. A travel mode other than driving alone, such as buses, rail transit, carpools, and vanpools.
Ridgeline. A line connecting the highest points along a ridge and separating drainage basins or small-scale drainage systems from one another.
Right-of-Way. A strip of land occupied or intended to be occupied by certain transportation and public use facilities, such as roads, railroads, and utility lines.
Riparian Corridor. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Riparian Lands. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Rooming or Boarding House. A dwelling or part of a dwelling where lodging is furnished for compensation to five or more persons living independently from each other. Meals may also be included. Does not include fraternities, sororities, convents, or monasteries, which are separately defined under "Organizational House."
Runoff. See "Landscaping Standards."
S Definitions, "S."
Sanitary Landfill. The controlled placement of refuse within a limited area, followed by compaction and covering with a suitable thickness of earth and other containment material.
Sanitary Sewer. A system of subterranean conduits that carries refuse liquids or waste matter to a plant where the sewage is treated, as contrasted with storm drainage systems (that carry surface water) and septic tanks or leech fields (that hold refuse liquids and waste matter on-site). (See "Combined Sewer" and "Septic System.")
Scenic Highway Corridor. The area outside a highway right-of-way that is generally visible to persons traveling on the highway.
Scenic Highway/Scenic Route. A highway, road, drive, or street that, in addition to its transportation function, provides opportunities for the enjoyment of natural and man-made scenic resources and access or direct views to areas or scenes of exceptional beauty or historic or cultural interest. The aesthetic values of scenic routes often are protected and enhanced by regulations governing the development of property or the placement of outdoor advertising. Until the mid-1980s, general plans in California were required to include a Scenic Highways element.
School. A public or private academic educational institution, including:
|
• boarding school • community college, college, or university • elementary, middle, and junior high schools |
|
• high school • military academy |
Also includes schools providing specialized education/training. Examples include the following:
|
• art school • ballet and other dance school • business, secretarial, and vocational school • computers and electronics school • drama school • driver education school • establishments providing courses by mail |
|
• language school • martial arts • music school • professional school (law, medicine, etc.) • seminaries/religious ministry training facility |
Also includes facilities, institutions and conference centers that offer specialized programs in personal growth and development, such as fitness, environmental awareness, arts, communications, and management. Does not include pre-schools and child day care facilities (see "Day Care"). See also the definition of "Studios - Art, Dance, Martial Arts, Music, etc." for smaller-scale facilities offering specialized instruction.
Scrap and Dismantling Yards. See "Recycling Facility."
Second Hand Store. A retail store that buys and sells used products, including clothing, furniture and household goods, jewelry, appliances, musical instruments, business machines and office equipment, tools, motors, machines, instruments, firearms, or any similar secondhand articles or objects. Does not include bookstores ("Retail Stores"); secondhand farm and construction equipment ("Construction, Farm, and Heavy Equipment Sales"); junk dealers, or scrap/dismantling yards ("Recycling Facilities - Scrap and Dismantling Yards"); the sale of antiques and collectibles ("Retail Stores"); the sale of cars and other used vehicles ("Auto and Vehicle Sales, Leasing, and Rental, Used"); or pawnshops ("Personal Services - Restricted").
Second Unit. See "Accessory Dwelling Unit."
Secretary of the Interior’s Standards. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Sediment Detention Basin. See "Grading."
Seiche. An earthquake-generated wave in an enclosed body of water such as a lake, reservoir, or bay.
Seismic. Caused by or subject to earthquakes or earth vibrations.
Seniors. Persons of age 62-years and older.
Senior Housing. Typically one- and two-bedroom apartments or condominiums designed to meet the needs of persons 62 years of age and older or, if more than 150 units, persons 55 years of age and older, and restricted to occupancy by them. (See also, "Congregate Care.")
Septic System. A sewage-treatment system that includes a settling tank through which liquid sewage flows and in which solid sewage settles and is decomposed by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. Septic systems are often used for individual-home waste disposal where an urban sewer system is not available. (See "Sanitary Sewer.")
Service Infrastructure. Small structures and infrastructure incidental to the primary structures on a site, which include, but are not limited to, mechanical equipment, solid waste and recycling enclosures, fencing, walls and gates, outdoor storage, and lighting. Service infrastructure also includes site structures, including but not limited to paving and surfacing, parking, loading, Americans with Disabilities Act site improvements, landscaping, and Low Impact Development features.
Service Station. A retail business selling vehicle fuels and related products; a card lock station is also included within this definition. Where allowed by Article 2 (Zoning Districts and Allowable Land Uses), a service station may also include: a convenience store; a restaurant, cafe, or coffee shop; minor maintenance and repair facility; tow truck operation; vehicle or trailer rentals; and fuel dealer sales.
Setback. The distance by which a structure, parking area or other development feature must be separated from a lot line, Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA), other structure or development feature, or street centerline. See also "Yard," and Section 9.30.090 (Setback Regulations and Exceptions).
Settlement. 1. The drop in elevation of a ground surface caused by settling or compacting. 2. The gradual downward movement of an engineered structure due to compaction. Differential settlement is uneven settlement, where one part of a structure settles more or at a different rate than another part.
Sex-Oriented Business. A business based upon materials or performances that depict, describe, or relate to sexual anatomical areas or activities. Sex oriented business shall not include the following: any activity conducted in private, including viewing NC-17-rated material in a private motel room through use of a satellite dish or other technology; creation and display of life or figure art in artist studios and artisan shops; selling or renting NC-17-rated movies, reading materials or other merchandise within a general video store, bookstore, or other retail store; and occasionally showing NC-17-rated movies or plays within a general movie or live theater.
Shall. That which is mandatory; an unequivocal direction.
Shared Living. The occupancy of a dwelling unit by persons of more than one family in order to reduce housing expenses and provide social contact, mutual support, and assistance. Shared living facilities serving six or fewer persons are permitted in all residential districts by ’1566.3 of the California Health and Safety Code.
Shopping Center. A primarily retail commercial site with three or more separate businesses sharing common pedestrian and parking areas.
Short Form [Erosion and Sediment Control Plan]. See "Grading."
Should. Signifies a directive to be honored if at all possible; a less rigid directive than "shall," to be honored in the absence of compelling or contravening considerations.
Sign. A structure, device, figure, display, message placard, or other contrivance excluding merchandise display, or any part thereof, located outdoors or indoors, that is designed, constructed, intended, or used to provide information, convey an idea, to direct or attract attention to an object, person, institution, business, product, service, event, or location by any means, including words, letters, figures, designs, symbols, fixtures, colors, illumination, or projected images. Does not include murals, paintings and other works of art that are not intended to otherwise advertise or identify any business or product. Types of signs include the following.
1. Abandoned Sign. A sign that no longer advertises a business, lessor, owner, product, service or activity on the premises where the sign is displayed.
2. Animated or Moving Sign. A sign which uses movement, lighting, or special materials to depict action or create a special effect to imitate movement.
3. Awning Sign. A sign copy or logo attached to or painted on an awning.
4. Banner, Flag, or Pennant. Cloth, bunting, plastic, paper, or similar non-rigid material used for advertising purposes attached to a structure, staff, pole, line, framing, or vehicle, not including official flags of the United States, the State of California, and other states of the nation, counties, municipalities, official flags of foreign nations and nationally or internationally recognized organizations.
5. Bench Sign. Copy painted on a portion of a bench.
6. Cabinet Sign (Can Sign). A sign which contains all the text and/or logo symbols within a single enclosed cabinet and may or may not be internally illuminated.
7. Changeable Copy Sign. A sign designed to allow the changing of copy through manual, mechanical, or electrical means including time and temperature.
8. Directional Sign. A sign that is designed and erected solely for the purposes of directing vehicular and/or pedestrian traffic within a project.
9. Directory Sign. A sign for listing the tenants and their suite numbers of a multiple tenant structure or center.
10. Double-Faced Sign. A sign constructed to display its message on the outer surfaces of two identical and/or opposite parallel planes.
11. Electronic Reader Board Sign. A sign with a fixed or changing display composed of a series of lights, but not including time and temperature displays.
12. Flashing Sign. A sign that contains an intermittent or sequential flashing light source.
13. Freestanding Sign. A sign fixed in an upright position on the ground not attached to a structure other than a framework, pole or device, erected primarily to support the sign. Includes monument signs and pole signs.
14. Prohibited Sign. A sign that includes any of the following:
a. A sign erected without complying with all regulations in effect at the time of its construction or use;
b. A sign that was legally erected, but whose use has ceased, the structure upon which the display is placed has been abandoned by its owner, or the sign is not being used to identify or advertise an ongoing business for a period of not less than 90 days;
c. A sign that was legally erected which later became nonconforming as a result of the adoption of an ordinance, if the amortization period for the display provided by the ordinance rendering the display conforming has expired, and conformance has not been accomplished;
d. A sign that was legally erected which later became nonconforming and then was damaged to the extent of more than 50 percent of its current replacement cost;
e. A sign which is a danger to the public or is unsafe;
f. A sign which is a traffic hazard not created by relocation of streets or highways or by acts of the City; or
g. A sign that pertains to a specific event, and 10 days have elapsed since the occurrence of the event.
15. Indirectly Illuminated Sign. A sign whose light source is external to the sign and which casts its light onto the sign from some distance.
16. Internally Illuminated Sign. A sign whose light source is located in the interior of the sign so that the rays go through the face of the sign, or light source which is attached to the face of the sign and is perceived as a design element of the sign.
17. Marquee (Canopy) Sign. A sign which is attached to or otherwise made a part of a permanent roof-like structure which projects beyond the building wall in the form of a large canopy to provide protection from the weather.
18. Monument Sign. An independent, freestanding structure supported on the ground having a solid base as opposed to being supported by poles or open braces.
19. Multi-Tenant Sign. An identification sign for a commercial site with multiple tenants, displaying the names of each tenant on the site.
20. Nonconforming Sign. A permanent or temporary advertising structure or sign which was legally established and maintained in compliance with the provisions of all applicable laws in effect at the time of original installation but that does not now comply with the provisions of this Land Use Code.
21. Obscene Sign. A sign that is offensive or repulsive to the senses, or is indecent or lewd.
22. Off-Site Directional Sign. A sign identifying a publicly owned facility, emergency facility, or a temporary subdivision sign, but excluding real estate signs.
23. Off-Site Sign. A sign identifying a use, facility, service, or product which is not located, sold, or manufactured on the same premise as the sign or which identifies a use, service, or product by a brand name which, although sold or manufactured on the premise, does not constitute the principal item for sale or manufactured on the premise.
24. Permanent Sign. A sign constructed of durable materials and intended to exist for the duration of time that the use or occupant is located on the premises.
25. Political Sign. A sign designed for the purpose of advertising support of or opposition to a candidate or proposition for a public election.
26. Pole/Pylon Sign. An elevated freestanding sign, typically supported by one or two poles or columns.
27. Portable Sidewalk Sign. An "a-frame" or "sandwich board" sign.
28. Portable Sign. A sign that is not permanently affixed to a structure or the ground.
29. Projecting Sign. A sign other than a wall sign suspending from, or supported by, a structure and projecting outward.
30. Real Estate Sign. A sign indicating that a property or any portion thereof is available for inspection, sale, lease, rent, or directing people to a property, but not including temporary subdivision signs.
31. Roof Sign. A sign constructed upon or over a roof, or placed so as to extend above the edge of the roof.
32. Temporary Sign. A sign intended to be displayed for a limited period of time and capable of being viewed from a public right-of-way, parking area or neighboring property.
33. Vehicle Sign. A sign attached to or suspended from a boat, vehicle, or other movable object that is parked within a public right-of-way, or located on private property but visible from a public right-of-way; except a sign painted directly upon, magnetically affixed to, or permanently affixed to the body or other integral part of a vehicle.
34. Wall Sign. A sign which is attached to or painted on the exterior wall of a structure with the display surface of the sign approximately parallel to the building wall.
35. Window Sign. A sign posted, painted, placed, or affixed in or on a window exposed to public view. An interior sign which faces a window exposed to public view and is located within three feet of the window.
Sign Area. The entire area within a perimeter defined by a continuous line composed of right angles using no more than four lines which enclose the extreme limits of lettering, logo, trademark, or other graphic representation.
Sign Height. The vertical distance from the uppermost point used in measuring the area of a sign to the average grade immediately below the sign, including its base or the top of the nearest curb of the street on which the sign fronts, whichever measurement is the greatest.
Significance. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Significant Architectural Features. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Significant Effect. A beneficial or detrimental impact on the environment. May include, but is not limited to, significant changes in an area’s air, water, and land resources.
Siltation. (1) The accumulating deposition of eroded material. (2) The gradual filling in of streams and other bodies of water with sand, silt, and clay.
Silviculture. See "Trees."
Single-Family Dwelling. A building designed for and/or occupied exclusively by one family. Also includes factory-built, modular housing units, constructed in compliance with the Uniform Building Code (UBC), and mobile homes/manufactured housing units that comply with the National Manufactured Housing Construction and Safety Standards Act of 1974, placed on permanent foundation systems. Includes transitional housing and supportive housing serving six or fewer persons (see "Shared Living").
Site. A parcel or adjoining parcels under single ownership or single control, considered a unit for the purposes of development or other use.
Site Coverage. The percentage of total site area occupied by structures, parking, pavement and driveways. Structure or building coverage includes the primary structure, all accessory structures (e.g., carports, garages, patio covers, storage sheds, trash dumpster enclosures, etc.) and any covered feature. Structure/building coverage is measured from exterior wall to exterior wall. Planted parking strips and pervious pavers are not counted as site coverage.
Small Family Day Care Home. See "Day Care."
Social Service Organization. A public or quasi-public establishment providing social and/or rehabilitation services, serving persons with social or personal problems requiring special services, the handicapped, and the otherwise disadvantaged. Examples of this land use include: counseling centers, welfare offices, job counseling and training centers, or vocational rehabilitation agencies. Includes organizations soliciting funds to be used directly for these and related services, and establishments engaged in community improvement and neighborhood development. Does not include day-care services, emergency shelters and transitional housing, or "Residential Care," which are separately defined.
Solar Access. The following terms and phrases are defined for the purposes of Chapter 9.56 (Solar Siting and Solar Access).
1. Adequate Solar Access. Building orientation such that the south sloped roof and wall down to ground level of the principal building on the lot, shall not be shaded more than 10 percent between the hours of 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. at any time throughout the year.
2. Solar Easement. The right of receiving sunlight across the real property of another for any solar energy system.
3. Solar Energy System. A solar energy system includes the following:
a. A solar collector or other solar energy device with its primary purpose to provide for the collection, storage, and distribution of solar energy for space heating, space cooling, electric generation, or water heating.
b. A structural design feature of a building, the primary purpose of which is to provide for the collection, storage, and distribution of solar energy for electricity generation, space heating or cooling, or for water heating.
4. Burdened Property. Property for which development restrictions are placed or proposed, in order to protect solar access to benefitted property.
5. Benefited Property. Property for which solar access protection is granted or proposed.
6. Due South. The direction of the south terrestrial pole.
7. Solar System, Active. A system using a mechanical device, such as a pump or a fan, and energy in addition to solar energy to transport a conductive medium (air or water) between a solar collector and the interior of a building for the purpose of heating or cooling.
8. Solar System, Passive. A system that uses direct heat transfer from thermal mass instead of mechanical power to distribute collected heat. Passive systems rely on building design and materials to collect and store heat and to create natural ventilation for cooling.
Solid Waste. Any unwanted or discarded material that is not a liquid or gas. Includes organic wastes, paper products, metals, glass, plastics, cloth, brick, rock, soil, leather, rubber, yard wastes, and wood, but does not include sewage and hazardous materials. Organic wastes and paper products comprise about 75% of typical urban solid waste.
Solid Waste Transfer Station. A facility for the temporary storage of municipal refuse prior to its transport to a landfill or other terminal disposal or recycling facility.
Sphere of Influence. The probable physical boundaries and service area of a local agency, as determined by the Local Agency Formation Commission (LAFCO) of the County.
Sports and Entertainment Assembly. A large-scale indoor or outdoor facility accommodating spectator-oriented sports, concerts, and other entertainment activities. Examples of this land use include amphitheaters, race tracks, stadiums and coliseums. May also include commercial facilities customarily associated with the above uses, including bars and restaurants, gift shops, video game arcades, etc.
Sports and Active Recreation Facility. Public and private facilities for various outdoor sports and other types of recreation, where the facilities are oriented more toward participants than spectators. Examples include:
|
• athletic/sport fields (e.g., baseball, football, softball, soccer) • health and athletic club outdoor facilities |
|
• skateboard parks • swimming pools • tennis and other sport courts (e.g., handball, squash) |
Stabilization. See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Standards. A rule or measure establishing a level of quality or quantity in a General Plan that must be complied with or satisfied. Examples of Standards might include: the number of acres of parkland per 1,000 population that a community will attempt to acquire and improve; the land use density for a designated land use category; or the traffic Level of Service (LOS) that a General Plan hopes to attain. Also see "Development Standards".
State Historical Building Code (SHBC). See "Historical Resource Preservation."
Stem Basal Area. See "Trees."
Storage - Accessory. The indoor storage of materials accessory and incidental to a primary use is not considered a land use separate from the primary use.
Storage - Business Records. A commercial storage facility specializing in the storage of business records.
Storage - Outdoor. An area not within a building that is proposed or used for the storage of building materials, other supplies, equipment, or other materials, either as the primary use of a parcel or as storage accessory to another use.
Storage - Personal Storage Facility (Mini-storage). Structures containing generally small, individual, compartmentalized stalls or lockers rented as individual storage spaces and characterized by low parking demand.
Storage - Storage Yard. The storage of various materials outside of a structure other than fencing, either as an accessory or primary use.
Storage - Warehouse, Indoor Storage. Facilities for the storage of furniture, household goods, or other commercial goods of any nature provided by moving companies. Includes cold storage. Does not include: warehouse, storage or mini-storage facilities offered for rent or lease to the general public ("Storage - Personal Storage Facility"); warehouse facilities primarily used for wholesaling and distribution (see "Wholesaling and Distribution"); or terminal facilities for handling freight (see "Truck or Freight Terminal").
Storie Index. A numerical system (0-100) rating the degree to which a particular soil can grow plants or produce crops, based on four factors: soil profile, surface texture, slope, and soil limitations. (See "Prime Agricultural Land.")
Storm Water Runoff. See "Grading."
Stream. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Stream Corridor. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Stream or Creek Bank. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Street. A thoroughfare which affords principal means of access to abutting property, including avenue, place, way, drive, lane, boulevard, highway, road, and any other thoroughfare except an alley as defined in this glossary. A public street is one that has been accepted by the City which has been constructed to City standards. (See also "Private Road/Private Street.")
Street Furniture. Those features associated with a street that are intended to enhance that street’s physical character and use by pedestrians, such as benches, trash receptacles, kiosks, lights, newspaper racks.
Street Tree Plan. A comprehensive plan for all trees on public streets that sets goals for solar access, and standards for species selection, maintenance, and replacement criteria, and for planting trees in patterns that will define neighborhood character while avoiding monotony or maintenance problems.
Street Trees. See "Trees."
Streets, Local. See " Streets, Minor."
Streets, Major. The transportation network that includes a hierarchy of freeways, arterials, and collectors to service through traffic.
Streets, Minor. Local streets not shown on the Circulation Plan, Map, or Diagram, whose primary intended purpose is to provide access to fronting properties.
Streets, Through. Streets that extend continuously between other major streets in the community.
Structure. Anything constructed or erected, the use of which requires attachment to the ground or attachment to something located on the ground. For the purposes of this Land Use Code, the term "structure" includes "signs" and "buildings," but does not include swimming pools, fences, walls used as fences, pens or corrals.
Studio - Art, Dance, Martial Arts, Music, etc. Small scale facilities, typically accommodating no more than three groups of students at a time. Larger facilities are included under the definition of "Schools - Specialized education and training." Examples of these facilities include: individual and group instruction and training in the arts; production rehearsal; photography, and the processing of photographs produced only by users of the studio facilities; martial arts training studios; gymnastics instruction, and aerobics and gymnastics studios with no other fitness facilities or equipment. Also includes production studios for individual musicians, painters, sculptors, photographers, and other artists.
Subdivision. The division, by any subdivider, of any unit or portion of land shown on the latest equalized Humboldt County assessment roll as a unit or contiguous units, for the purpose of sale, lease or financing, whether immediate or future. Property shall be considered as contiguous units, even if it is separated by roads, streets, utility easement or railroad rights-of-way. Subdivision includes the following, as defined in Civil Code Section 915: a condominium project; a community apartment project; or the conversion of five or more existing dwelling units to a stock cooperative.
Subdivision Map Act, or Map Act. Division 2, Title 7 of the California Government Code, commencing with Section 66410 as presently constituted, and any amendments to those provisions. This act vests in local legislative bodies the regulation and control of the design and improvement of subdivisions, including the requirement for tentative and final maps. (See also "Subdivision.")
Subsidence. The sudden sinking or gradual downward settling and compaction of soil and other surface material with little or no horizontal motion. Subsidence may be caused by a variety of human and natural activity, including earthquakes. (See "Settlement.")
Subsidize. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Substandard Housing. Residential dwellings that, because of their physical condition, do not provide safe and sanitary housing.
Substantial. Considerable in importance, value, degree, or amount.
Substantial Rehabilitation. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Surface Mining Operations. All or any part of the process involved in the mining of minerals on mined lands by removing overburden and mining directly from the mineral deposits, open pit mining of minerals naturally exposed, mining by the auger method, dredging and quarrying, or surface work incident to an underground mine.
Sustainability. Community use of natural resources in a way that does not jeopardize the ability of future generations to live and prosper.
Sustainable Development. Development that maintains or enhances economic opportunity and community wellbeing while protecting and restoring the natural environment upon which people and economies depend. Sustainable development meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. (Source: Minnesota State Legislature.)
T Definitions, "T."
Taking. A real estate term traditionally used to mean acquisition by eminent domain but broadened by the U.S. Supreme Court to mean any government action that denies all economically viable use of property.
Target Areas. Specifically designated sections of the community where loans and grants are made to bring about a specific outcome, such as the rehabilitation of housing affordable by very low- and low-income households.
Tax Increment. Additional tax revenues that result from increases in property values within a redevelopment area. State law permits the tax increment to be earmarked for redevelopment purposes but requires at least 20% to be used to increase and improve the community’s supply of very low- and low-income housing.
Telecommuting. An arrangement in which a worker is at home or in a location other than the primary place of work, and communicates with the workplace and conducts work via wireless or telephone lines, using modems, fax machines, or other electronic devices in conjunction with computers.
Telecommunications Facility. Public, commercial and private electromagnetic and photoelectrical transmission, broadcast, repeater and receiving stations for radio, television, telegraph, telephone, data network, and wireless communications, including commercial earth stations for satellite-based communications. Includes antennas, commercial satellite dish antennas, and equipment buildings. Does not include telephone, telegraph and cable television transmission facilities utilizing hard-wired or direct cable connections.
Temporary Structure. A structure without any foundation or footings, and which is removed when the designated time period, activity, or use for which the temporary structure was erected has ceased.
Temporary Use. A use of land that is designed, operated and occupies a site for a limited time, typically less than 12 months.
Theater, Auditorium. An indoor facility for public assembly and group entertainment, other than sporting events. Examples of these facilities include:
|
• civic theaters, and facilities for "live" theater and concerts • movie theaters |
|
• similar public assembly facilities • See also "Sports and Entertainment Assembly." |
Tidelands. Land subject to the ebb and flow of tides.
Top of Bank. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Topography. Configuration of a surface, including its relief and the position of natural and man-made features.
Tourism. The business of providing services for persons traveling for pleasure, tourism contributes to the vitality of the community by providing revenue to local business. Tourism can be measured through changes in the transient occupancy tax, or restaurant sales.
Townhouse; Townhome. A one-family dwelling in a row of at least three such units in which each unit has its own front and rear access to the outside, no unit is located over another unit, and each unit is separated from any other unit by one or more common and fire-resistant walls.
Traffic Model. A mathematical representation of traffic movement within an area or region based on observed relationships between the kind and intensity of development in specific areas. Many traffic models operate on the theory that trips are produced by persons living in residential areas and are attracted by various non-residential land uses. (See "Trip.")
Transit. The conveyance of persons or goods from one place to another by means of a local, public transportation system.
Transit, Public. A system of regularly-scheduled buses and/or trains available to the public on a fee-per-ride basis. Also called "Mass Transit."
Transit Station or Terminal. A passenger station for vehicular, and rail mass transit systems; also terminal facilities providing maintenance and service for the vehicles operated in the transit system. Includes buses, taxis, railway, etc.
Transitional Housing. Shelter provided to the homeless for an extended period, often as long as 24 months, and generally integrated with other social services and counseling programs to assist in the transition to self-sufficiency through the acquisition of stable income and permanent housing. (Also see "Emergency Shelter.")
Trees. Types of trees and related definitions include the following:
1. Arborist. 1) A person currently certified by the Western Chapter of the International Society of Arboriculture as an expert on the care of trees; 2) a consulting arborist who satisfies the requirements of the American Society of Consulting Arborists; or 3) other qualified professionals who the Director determines have gained through experience the qualifications to identify, remove, or replace trees.
2. Diameter of a Tree. Trunk diameter measured at 4.5 feet above the ground (also known as "Diameter at Breast Height," or "DBH).
3. Diseased Tree. A tree afflicted by, but not limited to, any of the following: insect infestation, heart rot, exfoliation, slime flux, crown rot, leaf scorch, root fungus, structural defects or weaknesses.
4. Drip line. A line that may be drawn on the ground around a tree directly under its outermost branch tips and which identifies that location where rainwater tends to drip from the trees. When depicted on a map, the drip line will appear as an irregular shaped circle that follows the contour of the tree’s branches as seen from overhead.
5. Forest Stand. A contiguous group of trees sufficiently uniform in species composition, arrangement of age classes and condition to be a distinguishable, homogeneous unit.
6. Hazardous Tree. A tree with structural defects likely to cause failure of all or part of the tree, which could strike a "target". A target can be a vehicle, building, or place where people gather such as a park bench, picnic table, street, or backyard. Hazardous defects are visible signs that the tree is failing. There are seven main types of tree defects: dead wood, cracks, weak branch unions, decay, cankers, root problems, and poor tree architecture. A tree with defects is not hazardous, however, unless some portion of it is within striking distance of a target.
7. Landmark Trees. Trees whose size, visual impact, or association with a historically significant structure or event have led the City or County to designate them as landmarks.
8. Natural Area. An area where no grading or development is permitted. For new and undeveloped lots subject to hillside development standards, a minimum of 50 percent of the area of each lot shall be designated as "natural area," and all areas with slopes greater than 25 percent shall be included in the "natural area."
9. Silviculture. The art, science, and practice of establishing, tending and reproducing forest stands of desired characteristics. It is based on knowledge of species characteristics and environmental requirements.
10. Stem Basal Area. The cross section area of the stem or stems of a plant or of all plants in a stand, generally expressed as square units per unit area. Tree basal is used to determine percent stocking. The cross section area of a tree stem in square feet commonly measured at breast height (4.5 feet above ground) and inclusive of bark, usually computed by using d.b.h. or tallied through the use of basal area factor angle gauge.
11. Street Trees. Trees strategically planted usually in parkway strips, medians, or along streets to enhance the visual quality of a street.
12. Stumpage. The value or volume of a tree or group of trees as they stand uncut in the woods (on the stump).
13. Topping. Cutting off the top section of a standing tree to the trunk. Topping is an injurious practice.
14. Trimming. The cutting of or removal of any limbs or branches of trees which will not seriously impair the health of trees. For the purposes of this code, the definition of trim shall not apply to any tree being grown as an orchard tree or other fruit or non-indigenous ornamental tree for which trimming and pruning are considered ordinary horticultural practices.
Trip. A one-way journey that proceeds from an origin to a destination via a single mode of transportation; the smallest unit of movement considered in transportation studies. Each trip has one "production end," (or origin-often from home, but not always), and one "attraction end," (destination). (See "Traffic Model.")
Trip Generation. The dynamics that account for people making trips in automobiles or by means of public transportation. Trip generation is the basis for estimating the level of use for a transportation system and the impact of additional development or transportation facilities on an existing, local transportation system. Trip generations of households are correlated with destinations that attract household members for specific purposes.
Truck Route. A path of circulation required for all vehicles exceeding set weight or axle limits, a truck route follows major arterials through commercial or industrial areas and avoids sensitive areas.
Truck or Freight Terminal. A transportation facility furnishing services incidental to air, motor freight, and rail transportation. Examples of these facilities include:
|
• freight forwarding services • freight terminal facilities • joint terminal and service facilities • overnight mail processing facilities • packing, crating, inspection and weighing services |
|
• postal service bulk mailing distribution centers • transportation arrangement services • trucking facilities, including transfer and storage |
Tsunami. A large ocean wave generated by an earthquake in or near the ocean.
U Definitions, "U."
Undevelopable. Specific areas where topographic, geologic, and/or surficial soil conditions indicate a significant danger to future occupants and a liability to the City or County are designated as "undevelopable" by the City or County.
Uniform Building Code (UBC). A national, standard building code that sets forth minimum standards for construction.
Uniform Housing Code (UHC). State housing regulations governing the condition of habitable structures with regard to health and safety standards, and which provide for the conservation and rehabilitation of housing in accordance with the Uniform Building Code (UBC).
Urban. Of, relating to, characteristic of, or constituting a city. Urban areas are generally characterized by moderate and higher density residential development (i.e., three or more dwelling units per acre), commercial development, and industrial development, and the availability of public services required for that development, specifically central water and sewer, an extensive road network, public transit, and other such services (e.g., safety and emergency response). Development not providing such services may be "non-urban" or "rural." (See "Urban Land Use.") CEQA defines "urbanized area" as an area that has a population density of at least 1,000 persons per square mile - (Public Resources Code Section 21080.14(b)).
Urban Design. The attempt to give form, in terms of both beauty and function, to selected urban areas or to whole cities. Urban design is concerned with the location, mass, and design of various urban components and combines elements of urban planning, architecture, and landscape architecture.
Urban Growth Boundary. An officially adopted and mapped line dividing land to be developed from land to be protected for natural or rural uses. Urban growth boundaries are regulatory tools, often designated for long periods of time (20 or more years) to provide greater certainty for both development and conservation goals.
Urban Land Use. Residential, commercial, or industrial land use in areas where urban services are available.
Urban Open Space. The absence of buildings or development, usually in well-defined volumes, within an urban environment.
Urban Services Boundary. A boundary, sometimes parcel-specific, located to mark the outer limit beyond which urban development will not be allowed. It has the aim of discouraging urban sprawl by containing urban development during a specified period, and its location may be modified over time.
Urban Service Area. (1) An area in which urban services will be provided and outside of which such services will not be extended. (2) Developed, undeveloped, or agricultural land, either incorporated or unincorporated, within the sphere of influence of a city, which is served or will be served during the first five years of an adopted capital improvement program by urban facilities, utilities, and services. The boundary around an urban service area is called the "urban service area boundary" and is to be developed in cooperation with a city and adopted by a Local Agency Formation Commission (LAFCO).
Urban Services. Utilities (such as water, gas, electricity, and sewer) and public services (such as police, fire, schools, parks, and recreation) provided to an urbanized or urbanizing area.
Urban Sprawl. Haphazard growth or outward extension of a city resulting from uncontrolled or poorly managed development.
Use, Primary. See "Primary Use."
Utility Corridors. Rights-of-way or easements for utility lines on either publicly or privately owned property. (See "Right-of-Way" or "Easement.")
Utility Facility. A fixed-base structure or facility serving as a junction point for transferring electric utility services from one transmission voltage to another or to local distribution and service voltages, and similar facilities for water supply and natural gas distribution. These uses include any of the following facilities that are not exempted from land use permit requirements by Government Code Section 53091:
|
• corporation and maintenance yards • electrical substations and switching stations • natural gas regulating and distribution facilities • public water system wells, treatment plants and storage • telephone switching facilities • wastewater treatment plants, settling ponds and disposal fields |
These uses do not include office or customer service centers (classified in "Offices").
Utility Infrastructure. Pipelines for water, natural gas, and sewage collection and disposal; and facilities for the transmission of electrical energy for sale, including transmission lines for a public utility company. Also includes telephone, telegraph, cable television and other communications transmission facilities utilizing direct physical conduits. Does not include offices or service centers (see "Offices - Business and Service"), or distribution substations (see "Utility Facility").
V Definitions, "V."
Vacation Rental. See "Lodging."
Vehicle Services. The repair, servicing, alteration, restoration, towing, painting, cleaning, or finishing of automobiles, trucks, recreational vehicles, boats and other vehicles as a primary use, including the incidental wholesale and retail sale of vehicle parts as an accessory use. This use includes the following categories:
1. Major Repair/Body Work. These establishments include towing, collision repair, other body work, and painting services.
2. Minor Maintenance/Repair. Minor facilities providing limited repair and maintenance services. Examples include: attended and self-service car washes; detailing services; muffler and radiator shops; quick-lube services; tire and battery sales and installation; and tire recapping and retreading within an enclosed structure.
Does not include automobile parking (see "Parking Facilities"), repair shops that are part of a vehicle dealership on the same site (see "Auto and Vehicle Sales and Rental," and "Mobile Home, RV, and Boat Sales and Rental"); service stations, which are separately defined; or dismantling yards, which are included under "Recycling - Scrap and Dismantling Yards."
Vehicle Storage. A service facility for the long-term storage of operative cars, trucks, buses, recreational vehicles, and other motor vehicles, for clients. Does not include dismantling yards (classified in "Recycling - Scrap and Dismantling Yards").
Very Low Income Household. See "Affordable and Inclusionary Housing."
Veterinary Clinics, Animal Hospitals. Office and indoor medical treatment facilities used by veterinarians, including large and small animal veterinary clinics, and animal hospitals. Does not include kennels and animal boarding, which are separately defined.
View Corridor. The line of sight-identified as to height, width, and distance-of an observer looking toward an object of significance to the community (e.g., ridgeline, river, historic building, etc.); the route that directs the viewer’s attention.
Viewshed. The area within view from a defined observation point.
W Definitions, "W."
Warehouse. See "Storage - Warehouse, Indoor Storage."
Warehouse Retail. A retail store that emphasizes the packaging and sale of products in large quantities or volumes, some at discounted prices, where products are typically displayed in their original shipping containers. Sites and buildings are usually large and industrial in character. Patrons may be required to pay membership fees.
Warehousing Use. A use engaged in storage, wholesale, and distribution of manufactured products, supplies, and equipment, excluding bulk storage of materials that are flammable or explosive or that present hazards or conditions commonly recognized as offensive.
Watercourse. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Water Feature. See "Landscaping Standards."
Watershed. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Wetland. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Wetland Buffer Area. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Wetland Delineation. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Wetland Setback. See "Environmentally Sensitive Habitat Area (ESHA)".
Wholesaling and Distribution. Establishments engaged in selling merchandise to retailers; to contractors, industrial, commercial, institutional, farm, or professional business users; to other wholesalers; or acting as agents or brokers in buying merchandise for or selling merchandise to such persons or companies. Examples of these establishments include:
|
• agents, merchandise or commodity brokers, and commission merchants • assemblers, buyers and associations engaged in the cooperative marketing of farm products • merchant wholesalers • stores primarily selling electrical, plumbing, heating and air conditioning supplies and equipment. |
Also includes storage, processing, packaging, and shipping facilities for mail order and e-commerce retail establishments.
Wildlife. Animals or plants existing in their natural habitat.
Wildlife Refuge. An area maintained in a natural state for the preservation of both animal and plant life.
Williamson Act. The term "Williamson Act" means California Government Code Section 51200 et seq., as they may be amended from time to time. Known formally as the California Land Conservation Act of 1965, it was designed as an incentive to retain prime agricultural land and open space in agricultural use, thereby slowing its conversion to urban and suburban development. The program entails a ten-year contract between the City or County and an owner of land whereby the land is taxed on the basis of its agricultural use rather than its market value. The land becomes subject to certain enforceable restrictions, and certain conditions need to be met prior to approval of an agreement.
Windmill. A tower and propeller assembly used to transform wind energy into mechanical energy for generating electricity or pumping water.
Wine Tasting. A facility, or area within a winery where wine and related products are offered for retail sale, where wine may be tasted for a fee, or without charge.
Winery. A manufacturing facility where wine grapes are crushed, and their juice is fermented, aged, bottled, and sold at wholesale as finished wine. May include tasting and accessory retail sales of wine produced on site.
Woodlands. Lands covered with woods or trees.
X Definitions, "X."
Xeriscaping. The environmental site design and consideration of drought-resistant plants that support water efficient landscaping, thereby promoting the concept of water conservation in the design of a project.
Y Definitions, "Y."
Yard. An area between a lot line and a structure, unobstructed and unoccupied from the ground upward, except for projections permitted by this Land Use Code. See also "Setback," and Section 9.30.090 (Setback Regulations and Exceptions).
1. Front Yard. An area extending across the full width of the lot between the front lot line and the primary structure.
2. Rear Yard. An area extending the full width of the lot between a rear lot line and the primary structure.
3. Side Yard. An area between a side lot line and the primary structure extending between the front and rear yards.
Z Definitions, "Z."
Zero Lot Line. The location of a building on a lot in such a manner that one or more building sides rests directly on a lot line.
Zone, Combining. A special purpose zone that is superimposed over the regular zoning map. Combining zones are used for a variety of purposes, such as, flood plain, wetlands protection, or historic designation. Also called "overlay zone."
Zone, Interim. A zoning designation that temporarily reduces or freezes allowable development in an area until a permanent classification can be fixed; generally assigned during General Plan preparation to provide a basis for permanent zoning.
Zoning. The division of a city or county by legislative regulations into areas, or zones, that specify allowable uses for real property and size restrictions for buildings within these areas; a program that implements policies of the General Plan.
Zoning Administrator. The City of Arcata Community Development Director, or designee of the Director.
Zoning District. Any of the residential, commercial, public, or overlay districts established by Article 2 (Zoning Districts and Allowable Land Uses), within which certain land uses are allowed or prohibited, and certain site planning and development standards are established (e.g., setbacks, height limits, site coverage requirements, etc.). A portion of the territory of a city or county within which uniform zoning regulations and requirements apply; a zone.
Zoning Map. Government Code Section 65851 permits a legislative body to divide a county, a city, or portions thereof, into zones of the number, shape, and area it deems best suited to carry out the purposes of the zoning ordinance. These zones are delineated on a map or maps, called the Zoning Map. (Ord. 1392, eff. 5/15/2009; Ord. 1419, eff. 10/5/2012; Ord. 1435, eff. 12/6/2013; Ord. 1484, eff. 3/17/2017; Ord. 1496, eff. 12/20/2017; Ord. 1501, eff. 7/6/2018; Ord. 1513, eff. 3/8/2019; Ord. 1516, eff. 8/16/2019; Ord. 1546, eff. 7/16/2021)
“Permanent food facility” and “ready-to-eat food” are used here as defined in the California Retail Food Code, Health and Safety Code Division 104, Part 7.


